Cord blood genomic analysis highlights the role of redox balance
- PMID: 20566327
- PMCID: PMC2921475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.05.026
Cord blood genomic analysis highlights the role of redox balance
Abstract
Neonates are exposed to elevated levels of reactive oxygen species as they transition from a hypoxic intrauterine to a normoxic extrauterine environment at birth. This increased oxidative stress is associated with neonatal morbidity. Current antioxidant supplementation treatment strategies have yet to translate into improved neonatal outcomes. Our understanding of a newborn's intricate redox balance, particularly at the genomic level, remains limited. Here, we performed genomic microarray analyses (approximately 14,500 genes) on extracted mRNA from umbilical cord whole blood at term gestation (n=10). Bioinformatic analyses identified 282 genes (2.0%) that were consistently present within the highest quintile of expressed genes. These genes were highly associated with oxidant stress and included superoxide dismutase 1, catalase, peroxiredoxins, and uncoupling proteins. Pathway analyses identified statistically significantly overrepresented functional pathways including "oxidative stress," "oxidative stress response mediated by nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor," "hypoxia-inducible factor signaling," and "mitochondrial dysfunction" (p<0.05). These results suggest that neonates require high levels of antioxidants and an intricate cellular redox balance to ensure a successful transition to the extrauterine environment. Understanding the genes necessary to maintain this delicate redox balance may lead to the development of alternative treatment strategies.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
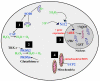
Free Radical Scavenging: Superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) scavenges oxygen free radicals while catalase (CAT) converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen.
Thioredoxin System: Peroxidredoxins reduce hydrogen peroxide by transferring electrons from thioredoxin (TRX) via PRDX2 or another donor such as glutathione via PRDX6 [25]
Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: Increased levels of ROS within the cellular milieu lead to an uncoupling and subsequent activation of Nrf2. Nrf2 then translocates to the nucleus, binds to ARE, and causes the upregulation of antioxidant genes such as glutathione transferase (GST), thioredoxin 1 (TR1), and NADPH:quinone oxidoreducatse-1 (NQO1) [23].
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Activation of UCP2 in the inner mitochondrial membrane diminishes the protonmotive force, attenuates mitochondrial ROS production, and reduces cellular oxidative stress damage [28].
Similar articles
-
Role of resveratrol in regulation of cellular defense systems against oxidative stress.Biofactors. 2018 Jan;44(1):36-49. doi: 10.1002/biof.1399. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Biofactors. 2018. PMID: 29193412 Review.
-
Downregulation of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor and Associated Antioxidant Genes Contributes to Redox-Sensitive Vascular Dysfunction in Hypertension.Hypertension. 2015 Dec;66(6):1240-50. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06163. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 26503970
-
Major differences in the levels of redox status and antioxidant defence markers in the erythrocytes of pre- and full-term neonates with intrauterine growth restriction.Reprod Toxicol. 2015 Jun;53:10-4. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Reprod Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25720296
-
Acute and prolonged effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GF424-derived SOD on antioxidant defense in healthy individuals challenged with intense aerobic exercise.Free Radic Biol Med. 2024 Nov 1;224:484-493. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.09.015. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39277120 Clinical Trial.
-
Maturation of the antioxidant system and the effects on preterm birth.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Aug;15(4):191-5. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 May 10. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010. PMID: 20452845 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization and non-parametric modeling of the developing serum proteome during infancy and early childhood.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 12;8(1):5883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24019-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29650987 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of oxidative stress markers in vaginal deliveries with or without epidural analgesia.Redox Rep. 2013;18(1):8-11. doi: 10.1179/1351000212Y.0000000034. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Redox Rep. 2013. PMID: 23321471 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Performing discovery-driven neonatal research by transcriptomic analysis of routinely discarded biofluids.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 Dec;25(12):2507-11. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2012.717126. Epub 2012 Aug 27. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012. PMID: 22920923 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of mitochondrial function in adult rat offspring of malnourished dams.World J Diabetes. 2011 Sep 15;2(9):149-57. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v2.i9.149. World J Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21954419 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Brain Injury Associated with a Model of Severe Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in Nonhuman Primates.Dev Neurosci. 2017;39(1-4):107-123. doi: 10.1159/000456658. Epub 2017 Mar 25. Dev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28343228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saugstad OD. Update on oxygen radical disease in neonatology. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001;13:147–153. - PubMed
-
- Friel JK, Friesen RW, Harding SV, Roberts LJ. Evidence of oxidative stress in full-term healthy infants. Pediatr. Res. 2004;56:878–882. - PubMed
-
- Signorini C, Perrone S, Sgherri C, Ciccoli L, Buonocore G, Leoncini S, Rossi V, Vecchio D, Comporti M. Plasma esterified F2-isoprostanes and oxidative stress in newborns: role of nonprotein-bound iron. Pediatr. Res. 2008;63:287–291. - PubMed
-
- O’Donovan DJ, Fernandes CJ. Free radicals and disease in premature infants. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2004;6:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Saugstad OD. Hypoxanthine as an indicator of hypoxia: its role in health and disease through free radical production. Pediatri. Res. 1988;23:143–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

