Laminin-121--recombinant expression and interactions with integrins
- PMID: 20566382
- PMCID: PMC2939186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.05.004
Laminin-121--recombinant expression and interactions with integrins
Abstract
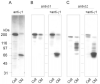
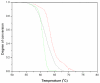
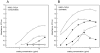
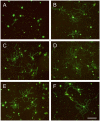
Laminin-121, previously referred as to laminin-3, was expressed recombinantly in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells by triple transfection of full-length cDNAs encoding mouse laminin α1, β2 and γ1 chains. The recombinant laminin-121 was purified using Heparin-Sepharose followed by molecular sieve chromatography and shown to be correctly folded by electron microscopy and circular dichroism (CD). The CD spectra of recombinant laminin-121 were very similar to those of laminin-111 isolated from Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm tumor (EHS-laminin) but its T(m) value was smaller than EHS-laminin and recombinant lamnin-111 suggesting that the replacement of the β chain reduced the stability of the coiled-coil structure of laminin-121. Its binding to integrins was compared with EHS-laminin, laminin-3A32 purified from murine epidermal cell line and recombinantly expressed laminins-111, -211 and -221. Laminin-121 showed the highest affinity to α6β1 and α7β1 integrins and furthermore, laminin-121 most effectively supported neurite outgrowth. Together, this suggests that the β2 laminins have higher affinity for integrins than the β1 laminins.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The C-terminal region of laminin beta chains modulates the integrin binding affinities of laminins.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 20;284(12):7820-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809332200. Epub 2009 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19147489 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-binding specificities of laminin-binding integrins: a comprehensive survey of laminin-integrin interactions using recombinant alpha3beta1, alpha6beta1, alpha7beta1 and alpha6beta4 integrins.Matrix Biol. 2006 Apr;25(3):189-97. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2005.12.001. Epub 2006 Jan 18. Matrix Biol. 2006. PMID: 16413178
-
Recognition of cryptic sites in human and mouse laminins by rat osteoclasts is mediated by beta 3 and beta 1 integrins.Bone. 1994 Nov-Dec;15(6):639-46. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(94)90312-3. Bone. 1994. PMID: 7532981
-
Molecular Basis of Laminin-Integrin Interactions.Curr Top Membr. 2015;76:197-229. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2015.07.002. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Curr Top Membr. 2015. PMID: 26610915 Review.
-
Laminins in lung development.Exp Lung Res. 1997 Mar-Apr;23(2):119-29. doi: 10.3109/01902149709074025. Exp Lung Res. 1997. PMID: 9088922 Review.
Cited by
-
Laminin isoforms and laminin-producing cells in rat anterior pituitary.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2012 Oct 31;45(5):309-15. doi: 10.1267/ahc.12028. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2012. PMID: 23209340 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow laminins influence hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell cycling and homing to the bone marrow.Matrix Biol. 2018 Apr;67:47-62. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29360499 Free PMC article.
-
Development of self-healing hydrogels to support choroidal endothelial cell transplantation for the treatment of early age related macular degeneration.Acta Biomater. 2025 Mar 1;194:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.12.052. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 39710218
-
Alignment and composition of laminin-polycaprolactone nanofiber blends enhance peripheral nerve regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012 Feb;100(2):406-23. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.33204. Epub 2011 Nov 21. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012. PMID: 22106069 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous laminin exhibits a unique vascular pattern in the brain via binding to dystroglycan and integrins.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022 Dec 3;19(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12987-022-00396-y. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022. PMID: 36463265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andac Z, Sasaki T, Mann K, Brancaccio A, Deutzmann R, Timpl R. Analysis of heparin, alpha-dystroglycan and sulfatide binding to the G domain of the laminin alpha1 chain by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;287:253–264. - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M, Nurcombe V, Edgar D, Paulsson M, Timpl R. The cellular interactions of laminin fragments. Cell adhesion correlates with two fragment-specific high affinity binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:11532–11538. - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M, Mann K, von der Mark H, Timpl R. Cell attachment properties of collagen type VI and Arg-Gly-Asp dependent binding to its alpha 2(VI) and alpha 3(VI) chains. Exp. Cell Res. 1989;181:463–474. - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Carter WG, Deutzmann R, Edger D, Ekblom P, Engel J, Engvall E, Hohenester E, Jones JCR, Kleinman HK, Marinkovich MP, Martin GR, Mayer U, Meneguzzi G, Miner JH, Miyazaki K, Patarroyo M, Paulsson M, Quaranta V, Sanes JR, Sasaki T, Sekiguchi K, Sorokin LM, Talts JF, Tryggvason K, Uitto J, Virtanen I, von der Mark K, Wewer UM, Yamada Y, Yurchenco PD. A simplified laminin nomenclature. Matrix Biol. 2005;24:326–332. - PubMed
-
- Bernier SM, Utani A, Sugiyama S, Doi T, Polistina C, Yamada Y. Cloning and expression of laminin alpha 2 chain (M-chain) in the mouse. Matrix Biol. 1995;14:447–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

