N-carbamylglutamate augments ureagenesis and reduces ammonia and glutamine in propionic acidemia
- PMID: 20566609
- PMCID: PMC3297024
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2010-0008
N-carbamylglutamate augments ureagenesis and reduces ammonia and glutamine in propionic acidemia
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to determine whether N-carbamylglutamate (NCG) reduces plasma levels of ammonia and glutamine and increases the rate of ureagenesis in patients with propionic acidemia (PA).
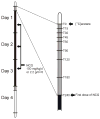
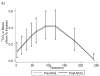
Methods: Identical 4-hour studies were performed before and immediately after a 3-day trial of oral NCG in 7 patients with PA. An oral bolus of [(13)C]sodium acetate was administered at the start of each study, and sequential blood samples were obtained to measure [(13)C]urea, ammonia, urea, and amino acids.
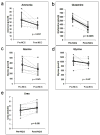
Results: With longitudinal mixed-effects linear regression, peak [(13)C]urea increased after treatment with NCG (from 2.2 to 3.8 microM; P < .0005). There were concomitant decreases in mean plasma ammonia (59-43 microM; P < .018) and glutamine (552-331 microM; P < .0005).
Conclusions: NCG augments ureagenesis and decreases plasma ammonia and glutamine in patients with PA. The drug may serve as an important therapeutic adjunct in the treatment of acute hyperammonemia in this disorder.
Figures

References
-
- Brusilow SW, Maestri NE. Urea cycle disorders: diagnosis, pathophysiology, and therapy. Adv Pediatr. 1996;43:127–70. - PubMed
-
- Batshaw ML, Brusilow S, Waber L, Blom W, Brubakk AM, Burton BK, et al. Treatment of inborn errors of urea synthesis: activation of alternative pathways of waste nitrogen synthesis and excretion. N Engl J Med. 1982;306(23):1387–92. - PubMed
-
- Batshaw ML, Brusilow SW. Treatment of hyperammonemic coma caused by inborn errors of urea synthesis. J Pediatr. 1980;97(6):893–900. - PubMed
-
- Hall LM, Metzenberg RL, Cohen PP. Isolation and characterization of a naturally occurring cofactor of carbamyl phosphate biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1958;230(2):1013–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK064913/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD061221/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK47870/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS054900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS054900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR019453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54RR-019453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01HD26979/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK64913/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD026979/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047870/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD058567/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD058567/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

