ATP overflow in skeletal muscle 1A arterioles
- PMID: 20566660
- PMCID: PMC2956947
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.193094
ATP overflow in skeletal muscle 1A arterioles
Abstract
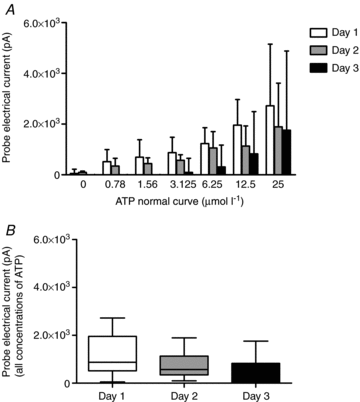
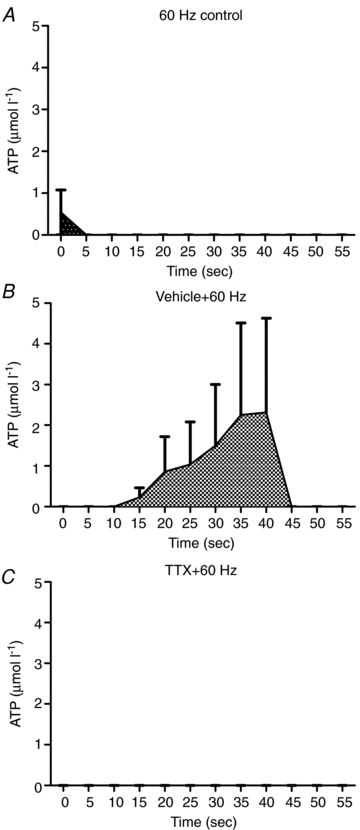
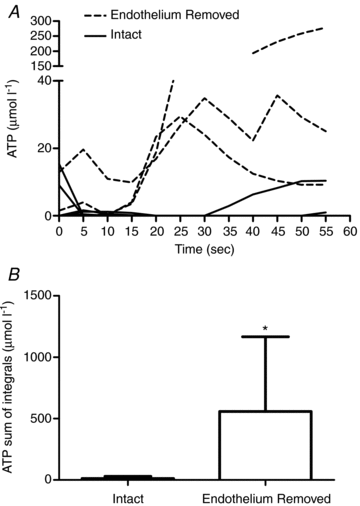
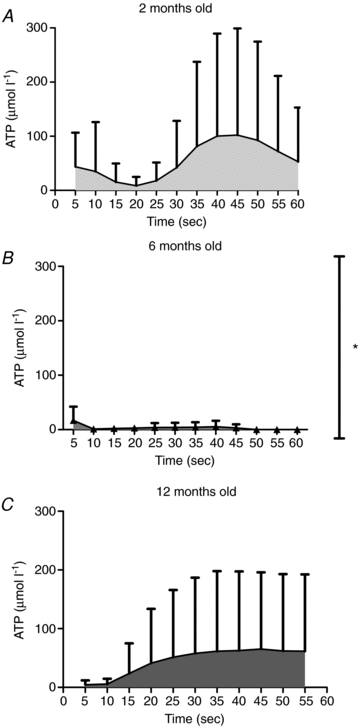
The purpose of this study was to investigate the sources of ATP in the 1A arteriole, and to investigate age-related changes in ATP overflow. Arterioles (1A) from the red portion of the gastrocnemius muscle were isolated, cannulated and pressurized in a microvessel chamber with field stimulation electrodes. ATP overflow was determined using probes specific for ATP and null probes that were constructed similar to the ATP probes, but did not contain the enzyme coating. ATP concentrations were determined using a normal curve (0.78 to 25 micromol l(-1) ATP). ATP overflow occurred in two phases. Phase one began in the first 20 s following stimulation and phase two started 35 s after field stimulation. Tetrodotoxin, a potent neurotoxin that blocks action potential generation in nerves, abolished both phases of ATP overflow. alpha1-Receptor blockade resulted in a small decrease in ATP overflow in phase two, but endothelial removal resulted in an increase in ATP overflow. ATP overflow was lowest in 6-month-old rats and highest in 12- and 2-month-old rats (P<0.05). ATP overflow measured via biosensors was of neural origin with a small contribution from the vascular smooth muscle. The endothelium seems to play an important role in attenuating ATP overflow in 1A arterioles.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Adrenergic control of vascular resistance varies in muscles composed of different fiber types: influence of the vascular endothelium.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):R783-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00205.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21677269 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathetic vasoconstrictor regulation of mouse colonic submucosal arterioles is altered in experimental colitis.J Physiol. 2007 Sep 1;583(Pt 2):719-30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.136838. Epub 2007 Jul 5. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17615098 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y overflow and metabolism in skeletal muscle arterioles.J Physiol. 2011 Jul 1;589(Pt 13):3309-18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.209726. Epub 2011 May 9. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21558160 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory and facilitatory presynaptic effects of endothelin on sympathetic cotransmission in the rat isolated tail artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jan;123(1):136-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701579. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9484864 Free PMC article.
-
Postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors are not present in proximal arterioles of rat intestine.Am J Physiol. 1998 Jan;274(1):H202-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1998.274.1.H202. Am J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9458869
Cited by
-
Use of Enzymatic Biosensors to Quantify Endogenous ATP or H2O2 in the Kidney.J Vis Exp. 2015 Oct 12;(104):53059. doi: 10.3791/53059. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26485400 Free PMC article.
-
The purinergic neurotransmitter revisited: a single substance or multiple players?Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Nov;144(2):162-91. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.05.012. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24887688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sources of intravascular ATP during exercise in humans: critical role for skeletal muscle perfusion.Exp Physiol. 2013 May;98(5):988-98. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2012.071555. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Exp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23315195 Free PMC article.
-
ATP metabolism in skeletal muscle arterioles.Physiol Rep. 2014 Jan 28;2(1):e00207. doi: 10.1002/phy2.207. eCollection 2014 Jan 1. Physiol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24744886 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of purine release with microelectrode biosensors.Purinergic Signal. 2012 Feb;8(Suppl 1):27-40. doi: 10.1007/s11302-011-9273-4. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Purinergic Signal. 2012. PMID: 22095158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao JX, Gonon F, Stjarne L. Kinetics of ATP- and noradrenaline-mediated sympathetic neuromuscular transmission in rat tail artery. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993;149:503–519. - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JB, Hamann JJ, Clifford PS. Vasoconstriction in active skeletal muscles: a potential role for P2X purinergic receptors. J Appl Physiol. 2003;95:953–959. - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JB, Taylor JC, Hamann JJ, Clifford PS. Do P2X purinergic receptors regulate skeletal muscle blood flow during exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286:H633–H639. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Current status of purinergic signalling in the nervous system. Prog Brain Res. 1999a;120:3–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

