SL2-like spliced leader RNAs in the basal nematode Prionchulus punctatus: New insight into the evolution of nematode SL2 RNAs
- PMID: 20566669
- PMCID: PMC2905750
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2155010
SL2-like spliced leader RNAs in the basal nematode Prionchulus punctatus: New insight into the evolution of nematode SL2 RNAs
Abstract
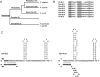
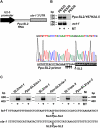
Spliced-leader (SL) trans-splicing has been found in all molecularly characterized nematode species to date, and it is likely to be a nematode synapomorphy. Most information regarding SL trans-splicing has come from the study of nematodes from a single monophyletic group, the Rhabditida, all of which employ SL RNAs that are identical to, or variants of, the SL1 RNA first characterized in Caenorhabditis elegans. In contrast, the more distantly related Trichinella spiralis, belonging to the subclass Dorylaimia, utilizes a distinct set of SL RNAs that display considerable sequence diversity. To investigate whether this is true of other members of the Dorylaimia, we have characterized SL RNAs from Prionchulus punctatus. Surprisingly, this revealed the presence of a set of SLs that show clear sequence similarity to the SL2 family of spliced leaders, which have previously only been found within the rhabditine group (which includes C. elegans). Expression of one of the P. punctatus SL RNAs in C. elegans reveals that it can compete specifically with the endogenous C. elegans SL2 spliced leaders, being spliced to the pre-mRNAs derived from downstream genes in operons, but does not compete with the SL1 spliced leaders. This discovery raises the possibility that SL2-like spliced leaders were present in the last common ancestor of the nematode phylum.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Resolution of polycistronic RNA by SL2 trans-splicing is a widely conserved nematode trait.RNA. 2020 Dec;26(12):1891-1904. doi: 10.1261/rna.076414.120. Epub 2020 Sep 4. RNA. 2020. PMID: 32887788 Free PMC article.
-
Spliced leader trans-splicing in the nematode Trichinella spiralis uses highly polymorphic, noncanonical spliced leaders.RNA. 2008 Apr;14(4):760-70. doi: 10.1261/rna.948008. Epub 2008 Feb 6. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18256244 Free PMC article.
-
Operon conservation and the evolution of trans-splicing in the phylum Nematoda.PLoS Genet. 2006 Nov 24;2(11):e198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020198. Epub 2006 Oct 9. PLoS Genet. 2006. PMID: 17121468 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of spliced leader trans-splicing in nematodes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1125-30. doi: 10.1042/BST0381125. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20659016 Review.
-
Nematode spliced leaders--ubiquity, evolution and utility.Int J Parasitol. 1996 Oct;26(10):1025-33. Int J Parasitol. 1996. PMID: 8982784 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterodera glycines utilizes promiscuous spliced leaders and demonstrates a unique preference for a species-specific spliced leader over C. elegans SL1.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1356. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37857-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30718603 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Insights into RNA trans-Splicing in Vertebrates.Genome Biol Evol. 2016 Mar 10;8(3):562-77. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw025. Genome Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 26966239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Possibility of an Early Evolutionary Origin for the Spliced Leader Trans-Splicing.J Mol Evol. 2017 Aug;85(1-2):37-45. doi: 10.1007/s00239-017-9803-y. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Mol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28744787 Review.
-
Operons are a conserved feature of nematode genomes.Genetics. 2014 Aug;197(4):1201-11. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.162875. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24931407 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-splicing and operons in C. elegans.WormBook. 2012 Nov 20:1-11. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.5.2. WormBook. 2012. PMID: 23175478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bird DM, Williamson VM, Abad P, McCarter J, Danchin EGJ, Castagnone-Sereno P, Opperman CH 2009. The genomes of root-knot nematodes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47: 333–351 - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal T 2005. Trans-splicing and operons. In Wormbook (ed. The C.elegans Research Community). WormBook. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.5.1. http://www.wormbook.org - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal T, Evans D, Link CD, Guffanti A, Lawson D, Thierry-Mieg J, Thierry-Mieg D, Chiu WL, Duke K, Kiraly M, et al. 2002. A global analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans operons. Nature 417: 851–854 - PubMed
-
- Davis RE 1997. Surprising diversity and distribution of spliced leader RNAs in flatworms. Mol Biochem Parasitol 87: 29–48 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
