Dapagliflozin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
- PMID: 20566676
- PMCID: PMC2945163
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0612
Dapagliflozin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
Abstract
Objective: Dapagliflozin, a highly selective inhibitor of the renal sodium-glucose cotransporter-2, increases urinary excretion of glucose and lowers plasma glucose levels in an insulin-independent manner. We evaluated the efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes.
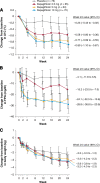
Research design and methods: This was a 24-week parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Patients with A1C 7.0-10% (n = 485) were randomly assigned to one of seven arms to receive once-daily placebo or 2.5, 5, or 10 mg dapagliflozin once daily in the morning (main cohort) or evening (exploratory cohort). Patients with A1C 10.1-12% (high-A1C exploratory cohort; n = 73) were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive blinded treatment with a morning dose of 5 or 10 mg/day dapagliflozin. The primary end point was change from baseline in A1C in the main cohort, statistically tested using an ANCOVA.
Results: In the main cohort, mean A1C changes from baseline at week 24 were -0.23% with placebo and -0.58, -0.77 (P = 0.0005 vs. placebo), and -0.89% (P < 0.0001 vs. placebo) with 2.5, 5, and 10 mg dapagliflozin, respectively. Signs, symptoms, and other reports suggestive of urinary tract infections and genital infection were more frequently noted in the dapagliflozin arms. There were no major episodes of hypoglycemia. Data from exploratory cohorts were consistent with these results.
Conclusions: Dapagliflozin lowered hyperglycemia in treatment-naive patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. The near absence of hypoglycemia and an insulin-independent mechanism of action make dapagliflozin a unique addition to existing treatment options for type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Comment in
-
Diabetes: Dapagliflozin: an insulin-independent, therapeutic option for type 2 diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010 Oct;6(10):531. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.134. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 21080534 No abstract available.
References
-
- The ADVANCE Collaborative Group Intensive glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2560–2572 - PubMed
-
- Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, Zieve FJ, Marks J, Davis SN, Hayward R, Warren SR, Goldman S, McCarren M, Vitek ME, Henderson WG, Huang GD: VADT Investigators Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2009;360:129–139 - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA: 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1577–1589 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

