A genetic resource for early-morning flowering trait of wild rice Oryza officinalis to mitigate high temperature-induced spikelet sterility at anthesis
- PMID: 20566680
- PMCID: PMC2924824
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcq124
A genetic resource for early-morning flowering trait of wild rice Oryza officinalis to mitigate high temperature-induced spikelet sterility at anthesis
Abstract
Background and aims: High temperatures over 32-36 degrees C at anthesis induce spikelet sterility in rice. The use of a germplasm with an early-morning flowering (EMF) trait has been hypothesized as a way of avoiding this problem. In this study, the effect of the EMF trait on avoiding high temperature-induced sterility at anthesis by flowering at a cooler temperature in the early morning was evaluated.
Methods: The EMF trait was introgressed from wild rice (Oryza officinalis) into the rice cultivar 'Koshihikari' (O. sativa). First, spikelets of the EMF line and Koshihikari were subjected to rising temperatures during the daytime in the greenhouse to test for differences in spikelet sterility. Secondly, spikelets of both plants were exposed to 26, 34 and 38 degrees C at anthesis and to 38 degrees C beginning at least 1 h after flowering, in the growth chambers at 70 % relative humidity, to test for differences in tolerance to high temperatures.
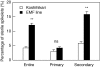
Key results: Spikelets of the EMF line started and completed flowering a few hours earlier than Koshihikari. In a greenhouse experiment, spikelets of Koshihikari opened after the air temperature reached 35 degrees C, but those of the EMF line could open at cooler temperatures. Under these conditions, spikelet sterility significantly increased in Koshihikari, but did not in the EMF line. The number of sterile spikelets increased as their flowering time was delayed in Koshihikari. Furthermore, the chamber experiments revealed that 60 % of the spikelets from both lines were sterile when exposed to 38 degrees C at anthesis, indicating that tolerance of high temperature was similar in both genotypes.
Conclusions: Reduced sterility in the EMF line subjected to rising temperatures at anthesis in the greenhouse was attributed to an earlier flowering time compared with Koshihikari. The EMF trait of wild rice is effective in mitigating anticipated yield loss due to global warming by escaping high-temperature stress at anthesis during the daytime.
Figures
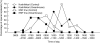
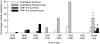
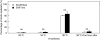
References
-
- Baker JT, Allen LH, Boote KJ. Temperature effects on rice at elevated CO2 concentration. Journal of Experimental Botany. 1992;43:959–964.
-
- Hasegawa T, Yoshimoto M, Kuwagata T, Ishigooka Y, Kondo M, Ishimaru T. The impact of global warming on rice production: lessons from spikelet sterility observed under the record hot summer of 2007. NIAES Annual Report 2008. 2009:23–25.
-
- Horie T. Predicting the effects of climatic variation and elevated CO2 on rice yield in Japan. Journal of Agricultural Metrology. 1993;48:567–574.
-
- IPCC. Working Group II. 4th Assessment Report, ‘Impacts, Adaptation and Valnerability’. 2007 http://www.ipcc-wg2.org/ . 7 October 2007.
-
- Jagadish SVK, Craufurd PQ, Wheeler TR. High temperature stress and spikelet fertility in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Journal of Experimental Botany. 2007;58:1627–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

