Synergistic activities of an efflux pump inhibitor and iron chelators against Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth and biofilm formation
- PMID: 20566773
- PMCID: PMC2935009
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00463-10
Synergistic activities of an efflux pump inhibitor and iron chelators against Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth and biofilm formation
Abstract
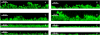
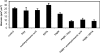
The efflux pump inhibitor phenyl-arginine-beta-naphthylamide (PAbetaN) was paired with iron chelators 2,2'-dipyridyl, acetohydroxamic acid, and EDTA to assess synergistic activities against Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth and biofilm formation. All of the tested iron chelators synergistically inhibited P. aeruginosa growth and biofilm formation with PAbetaN. PAbetaN-EDTA showed the most promising activity against P. aeruginosa growth and biofilm formation.
Figures
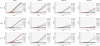

References
-
- Arruda, E. A., I. S. Marinho, M. Boulos, S. I. Sinto, H. H. Caiaffa, C. M. Mendes, C. P. Oplustil, H. Sader, C. E. Levy, and A. S. Levin. 1999. Nosocomial infections caused by multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 20:620-623. - PubMed
-
- Bodey, G. P., R. Bolivar, V. Fainstein, and L. Jadeja. 1983. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev. Infect. Dis. 5:279-313. - PubMed
-
- Clark, D. J., and O. Maaløe. 1967. DNA replication and the division cycle in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 23:99-112.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

