Smg1 is required for embryogenesis and regulates diverse genes via alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
- PMID: 20566848
- PMCID: PMC2901484
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1007336107
Smg1 is required for embryogenesis and regulates diverse genes via alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Abstract
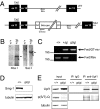
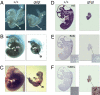
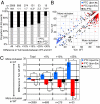
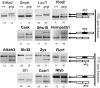
Smg1 is a PI3K-related kinase (PIKK) associated with multiple cellular functions, including DNA damage responses, telomere maintenance, and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). NMD degrades transcripts that harbor premature termination codons (PTCs) as a result of events such as mutation or alternative splicing (AS). Recognition of PTCs during NMD requires the action of the Upstream frameshift protein Upf1, which must first be phosphorylated by Smg1. However, the physiological function of mammalian Smg1 is not known. By using a gene-trap model of Smg1 deficiency, we show that this kinase is essential for mouse embryogenesis such that Smg1 loss is lethal at embryonic day 8.5. High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) of RNA from cells of Smg1-deficient embryos revealed that Smg1 depletion led to pronounced accumulation of PTC-containing splice variant transcripts from approximately 9% of genes predicted to contain AS events capable of eliciting NMD. Among these genes are those involved in splicing itself, as well as genes not previously known to be subject to AS-coupled NMD, including several involved in transcription, intracellular signaling, membrane dynamics, cell death, and metabolism. Our results demonstrate a critical role for Smg1 in early mouse development and link the loss of this NMD factor to major and widespread changes in the mammalian transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CK2-mediated TEL2 phosphorylation augments nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) by increase of SMG1 stability.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1829(10):1047-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23831331
-
SMG1 regulates adipogenesis via targeting of staufen1-mediated mRNA decay.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1829(12):1276-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24185201
-
Processing bodies are not required for mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.RNA. 2009 Jul;15(7):1265-73. doi: 10.1261/rna.1672509. Epub 2009 May 27. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19474145 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution and diversity of the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway.F1000Res. 2018 Aug 15;7:1299. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.15872.2. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 30345031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of SMG-1-mediated Upf1 phosphorylation in mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.Genes Cells. 2013 Mar;18(3):161-75. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12033. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Genes Cells. 2013. PMID: 23356578 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylxanthines Increase Expression of the Splicing Factor SRSF2 by Regulating Multiple Post-transcriptional Mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):14986-5003. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.624254. Epub 2015 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25818199 Free PMC article.
-
RNA metabolism and links to inflammatory regulation and disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec 31;79(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04073-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34971439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine-Tuning Amyloid Precursor Protein Expression through Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay.eNeuro. 2024 Jun 10;11(6):ENEURO.0034-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0034-24.2024. Print 2024 Jun. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 38789273 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA 433 regulates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by targeting SMG5 mRNA.BMC Mol Biol. 2016 Jul 29;17(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12867-016-0070-z. BMC Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27473591 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo determination of direct targets of the nonsense-mediated decay pathway in Drosophila.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Mar 20;4(3):485-96. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.009357. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 24429422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denning G, Jamieson L, Maquat LE, Thompson EA, Fields AP. Cloning of a novel phosphatidylinositol kinase-related kinase: Characterization of the human SMG-1 RNA surveillance protein. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:22709–22714. - PubMed
-
- Brumbaugh KM, et al. The mRNA surveillance protein hSMG-1 functions in genotoxic stress response pathways in mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 2004;14:585–598. - PubMed
-
- Azzalin CM, et al. Telomeric repeat containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends. Science. 2007;318:798–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

