Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns
- PMID: 20566857
- PMCID: PMC2900693
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002601107
Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns
Abstract
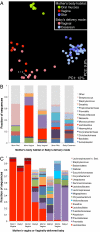
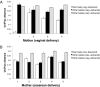
Upon delivery, the neonate is exposed for the first time to a wide array of microbes from a variety of sources, including maternal bacteria. Although prior studies have suggested that delivery mode shapes the microbiota's establishment and, subsequently, its role in child health, most researchers have focused on specific bacterial taxa or on a single body habitat, the gut. Thus, the initiation stage of human microbiome development remains obscure. The goal of the present study was to obtain a community-wide perspective on the influence of delivery mode and body habitat on the neonate's first microbiota. We used multiplexed 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing to characterize bacterial communities from mothers and their newborn babies, four born vaginally and six born via Cesarean section. Mothers' skin, oral mucosa, and vagina were sampled 1 h before delivery, and neonates' skin, oral mucosa, and nasopharyngeal aspirate were sampled <5 min, and meconium <24 h, after delivery. We found that in direct contrast to the highly differentiated communities of their mothers, neonates harbored bacterial communities that were undifferentiated across multiple body habitats, regardless of delivery mode. Our results also show that vaginally delivered infants acquired bacterial communities resembling their own mother's vaginal microbiota, dominated by Lactobacillus, Prevotella, or Sneathia spp., and C-section infants harbored bacterial communities similar to those found on the skin surface, dominated by Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, and Propionibacterium spp. These findings establish an important baseline for studies tracking the human microbiome's successional development in different body habitats following different delivery modes, and their associated effects on infant health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Additional maternal and nonmaternal factors contribute to microbiota shaping in newborns.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 19;107(42):E159; author reply E160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010526107. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20876088 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhou X, et al. Differences in the composition of vaginal microbial communities found in healthy Caucasian and black women. ISME J. 2007;1:121–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

