miR-33 links SREBP-2 induction to repression of sterol transporters
- PMID: 20566875
- PMCID: PMC2901433
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1005191107
miR-33 links SREBP-2 induction to repression of sterol transporters
Abstract
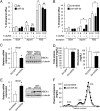
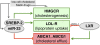
The sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBP-2) and the liver X receptor (LXR) control antagonistic transcriptional programs that stimulate cellular cholesterol uptake and synthesis, and cholesterol efflux, respectively. The clinical importance of SREBP-2 is revealed in patients with hypercholesterolemia treated with statins, which reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels by increasing hepatic expression of SREBP-2 and its target, the LDL receptor. Here we show that miR-33 is encoded within SREBP-2 and that both mRNAs are coexpressed. We also identify sequences in the 3' UTR of ABCA1 and ABCG1, sterol transporter genes both previously shown to be regulated by LXR, as targets for miR-33-mediated silencing. Our data show that LXR-dependent cholesterol efflux to both ApoAI and serum is ameliorated by miR-33 overexpression and, conversely, stimulated by miR-33 silencing. Finally, we show that ABCA1 mRNA and protein and plasma HDL levels decline after hepatic overexpression of miR-33, whereas they increase after hepatic miR-33 silencing. These results suggest novel ways to manage hypercholesterolemic patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors are pursuing a patent related to this work.
Figures
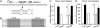

References
-
- Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis: The road ahead. Cell. 2001;104:503–516. - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W, et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee Heart disease and stroke statistics—2007 update: A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115:e69–e171. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Castelli WP, Gordon T. Cholesterol in the prediction of atherosclerotic disease: New perspectives based on the Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Baigent C, et al. Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaborators Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: Prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet. 2005;366:1267–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

