PDGF-CC blockade inhibits pathological angiogenesis by acting on multiple cellular and molecular targets
- PMID: 20566880
- PMCID: PMC2901428
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1004143107
PDGF-CC blockade inhibits pathological angiogenesis by acting on multiple cellular and molecular targets
Abstract
The importance of identifying VEGF-independent pathways in pathological angiogenesis is increasingly recognized as a result of the emerging drug resistance to anti-VEGF therapies. PDGF-CC is the third member of the PDGF family discovered after more than two decades of studies on PDGF-AA and PDGF-BB. The biological function of PDGF-CC and the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms remain largely unexplored. Here, using different animal models, we report that PDGF-CC inhibition by neutralizing antibody, shRNA, or genetic deletion suppressed both choroidal and retinal neovascularization. Importantly, we revealed that PDGF-CC targeting acted not only on multiple cell types important for pathological angiogenesis, such as vascular mural and endothelial cells, macrophages, choroidal fibroblasts and retinal pigment epithelial cells, but also on the expression of other important angiogenic genes, such as PDGF-BB and PDGF receptors. At a molecular level, we found that PDGF-CC regulated glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3beta phosphorylation and expression both in vitro and in vivo. Activation of GSK3beta impaired PDGF-CC-induced angiogenesis, and inhibition of GSK3beta abolished the antiangiogenic effect of PDGF-CC blockade. Thus, we identified PDGF-CC as an important candidate target gene for antiangiogenic therapy, and PDGF-CC inhibition may be of therapeutic value in treating neovascular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
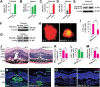
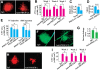
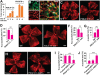
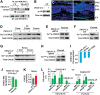
References
-
- Ferrara N. Pathways mediating VEGF-independent tumor angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010;21:21–26. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin LE, Hemo I, Keshet E. A plasticity window for blood vessel remodelling is defined by pericyte coverage of the preformed endothelial network and is regulated by PDGF-B and VEGF. Development. 1998;125:1591–1598. - PubMed
-
- Crawford Y, Ferrara N. Tumor and stromal pathways mediating refractoriness/resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30:624–630. - PubMed
-
- Li X, et al. PDGF-C is a new protease-activated ligand for the PDGF alpha-receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:302–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

