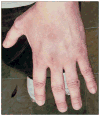
Persistent prurigo nodularis responsive to initiation of combination therapy with raltegravir
- PMID: 20566941
- PMCID: PMC4636204
- DOI: 10.1001/archdermatol.2010.128
Persistent prurigo nodularis responsive to initiation of combination therapy with raltegravir
Figures
References
-
- Zancanaro PC, McGirt LY, Mamelak AJ, Nguyen RH, Martins CR. Cutaneous manifestations of HIV in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: an institutional urban clinic experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(4):581–588. - PubMed
-
- Neri S, Ierna D, D’Amico RA, Giarratano G, Leotta C. Helicobacter pylori and prurigo nodularis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999;46(28):2269–2272. - PubMed
-
- Mattila JO, Vornanen M, Katila ML. Histopathological and bacteriological findings in prurigo nodularis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997;77(1):49–51. - PubMed
-
- Lee MR, Shumack S. Prurigo nodularis: a review. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46(4):211–220. - PubMed
-
- Markowitz M, Nguyen BY, Gotuzzo E, et al. Protocol 004 Part II Study Team. Rapid and durable antiretroviral effect of the HIV-1 Integrase inhibitor raltegravir as part of combination therapy in treatment-naive patients with HIV-1 infection: results of a 48-week controlled study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;46(2):125–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical