Effects of α-blocker 'add on' treatment on blood pressure in symptomatic BPH with or without concomitant hypertension
- PMID: 20567256
- PMCID: PMC3010011
- DOI: 10.1038/pcan.2010.19
Effects of α-blocker 'add on' treatment on blood pressure in symptomatic BPH with or without concomitant hypertension
Abstract
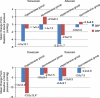
We investigated the effects of 'add on' treatment of α-blocker (AB) on blood pressure (BP) and the safety of ABs in men with symptomatic BPH with or without hypertension. We retrospectively reviewed 2,924 BPH outpatients who took ABs at our institution between 2005 and 2009. BPH symptom severity, prostate volume and BP were determined for 953 patients with their baseline data. BP level and International Prostate Symptom Score were measured within 2 months after AB treatment. Patients were assigned to four groups: group 1 had 272 normotensive patients on concomitant hypertensive medication; group 2 had 293 normotensive patients not on the medication; group 3 had 216 hypertensive patients on concomitant medication; and group 4 had 172 hypertensive patients not on the medication. The addition of AB lowered the mean systolic BP by 16.6 mm Hg for group 3 and by 8.6 mm Hg for group 4, and diastolic BP by 18.0 mm Hg for group 3 (P<0.05). However, normotensive groups on entry, irrespective of antihypertensive medication, showed no significant BP changes from baseline after AB medication. In the hypertensive groups on entry, the doxazosin gastrointestinal therapeutic system (GITS) resulted in significant reductions in systolic BP from 142.2 to 134.9 mm Hg and in diastolic BP from 97.6 to 84.6 mm Hg. When analyzed by AB regimen, the incidence of BP-related adverse events was comparable. AB therapy for BPH can have an appropriate and beneficial effect on BP, especially in baseline hypertensive patients. Doxazosin GITS treatment resulted in optimal management of BP within the normal range, especially in pharmacologically or physiologically hypertensive patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A multicenter, community-based study of doxazosin in the treatment of concomitant hypertension and symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: the Hypertension and BPH Intervention Trial (HABIT).Clin Ther. 1999 Oct;21(10):1732-48. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(99)80052-6. Clin Ther. 1999. PMID: 10566569
-
Long-term follow-up study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the doxazosin gastrointestinal therapeutic system in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia with or without concomitant hypertension.BJU Int. 2006 Jan;97(1):90-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.05858.x. BJU Int. 2006. PMID: 16336335
-
A randomized, double-blind crossover study of tamsulosin and controlled-release doxazosin in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia.BJU Int. 2003 Jan;91(1):41-4. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.03077.x. BJU Int. 2003. PMID: 12614248 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of doxazosin GITS on blood pressure in hypertensive and normotensive patients: a review of hypertension and BPH studies.Blood Press Suppl. 2003 May;1:5-13. doi: 10.1080/08038020310000078. Blood Press Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12800982 Review.
-
Patients with uncontrolled hypertension or concomitant hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia.Clin Cardiol. 2004 Feb;27(2):63-9. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960270203. Clin Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 14979621 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of silodosin in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in elderly men taking antihypertensive medications.Prostate Int. 2017 Sep;5(3):113-118. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Prostate Int. 2017. PMID: 28828355 Free PMC article.
-
Prostatic relaxation induced by loperamide is reduced in spontaneously hypertensive rats.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:941685. doi: 10.1100/2012/941685. Epub 2012 May 3. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22645476 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutical Approach to Arterial Hypertension - Current State of the Art.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(29):4602-4620. doi: 10.2174/0109298673274823231220063652. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38303535 Review.
-
Multicenter, prospective, comparative cohort study evaluating the efficacy and safety of alfuzosin 10 mg with regard to blood pressure in men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia with or without antihypertensive medications.Clin Interv Aging. 2015 Jan 17;10:277-86. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S74102. eCollection 2015. Clin Interv Aging. 2015. PMID: 25653511 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Naftopidil Treatment for Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Hypertension: A Prospective, Open-Label Study.Yonsei Med J. 2017 Jul;58(4):800-806. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.800. Yonsei Med J. 2017. PMID: 28540994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Tammela T. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. Practical treatment guidelines. Drugs Aging. 1997;10:349–366. - PubMed
-
- Boyle P, Napalkov P. The epidemiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia and observations on concomitant hypertension. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1995;168:7–12. - PubMed
-
- Parsons JK. Modifiable risk factors for benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms: new approaches to old problems. J Urol. 2007;178:395–401. - PubMed
-
- Chung BH, Hong SJ, Lee MS. Doxazosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia: an open-label, baseline-controlled study in Korean general practice. Int J Urol. 2005;12:159–165. - PubMed
-
- Fawzy A, Hendry A, Cook E, Gonzalez F. Long-term (4 year) efficacy and tolerability of doxazosin for the treatment of concurrent benign prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension. Int J Urol. 1999;6:346–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical