Molecular cloning and gene expression analysis of the leptin receptor in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis
- PMID: 20567508
- PMCID: PMC2887359
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011175
Molecular cloning and gene expression analysis of the leptin receptor in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis
Abstract
Background: Leptin is an adipocyte-derived hormone with multiple functions that regulates energy homeostasis and reproductive functions. Increased knowledge of leptin receptor function will enhance our understanding of the physiological roles of leptin in animals.
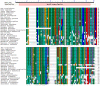
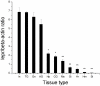
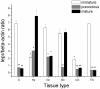
Methodology/principal findings: In the present study, a full-length leptin receptor (lepr) cDNA, consisting of 1,353 nucleotides, was cloned from Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) using rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) following the identification of a single expressed sequence tag (EST) clone in a cDNA library. The lepr cDNA consisted of a 22-nucleotide 5'-untranslated region (5' UTR), a 402-nucleotide open reading frame (ORF) and a 929-nucleotide 3' UTR. Multiple sequence alignments revealed that Chinese mitten crab lepr shared a conserved vacuolar protein sorting 55 (Vps55) domain with other species. Chinese mitten crab lepr expression was determined in various tissues and at three different reproductive stages using quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Lepr expression was highest in the intestine, thoracic ganglia, gonad, and accessory gonad, moderate in hepatopancreas and cranial ganglia, and low in muscle, gill, heart, haemocytes, and stomach. Furthermore, lepr expression was significantly higher in the intestine, gonad and thoracic ganglia in immature crabs relative to precocious and mature crabs. In contrast, lepr expression was significantly lower in the hepatopancreas of immature crabs relative to mature crabs.
Conclusions/significance: We are the first to identify the lepr gene and to determine its gene expression patterns in various tissues and at three different reproductive stages in Chinese mitten crab. Taken together, our results suggest that lepr may be involved in the nutritional regulation of metabolism and reproduction in Chinese mitten crabs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning, characterization and mRNA expression of copper-binding protein hemocyanin subunit in Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012 Nov;33(5):1222-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2012.09.023. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23032440
-
A prophenoloxidase from the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis: gene cloning, expression and activity analysis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008 Feb;24(2):156-67. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2007.08.006. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18160310
-
Molecular cloning and expression of a Relish gene in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis.Int J Immunogenet. 2010 Dec;37(6):499-508. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313X.2010.00954.x. Int J Immunogenet. 2010. PMID: 20670337
-
A putative endocrine factor SIBD (single insulin binding domain protein) involved in immune response of Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010 Jan;28(1):10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2009.09.013. Epub 2009 Sep 20. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19772924
-
A γ-aminobutyrate type A receptor-associated protein involved in the immune response of Eriocheir sinensis.Int J Immunogenet. 2012 Feb;39(1):46-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313X.2011.01044.x. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Int J Immunogenet. 2012. PMID: 22008098
Cited by
-
In silico Neuropeptidome of Female Macrobrachium rosenbergii Based on Transcriptome and Peptide Mining of Eyestalk, Central Nervous System and Ovary.PLoS One. 2015 May 29;10(5):e0123848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123848. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26023789 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for positive selection on the leptin gene in Cetacea and Pinnipedia.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026579. Epub 2011 Oct 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22046310 Free PMC article.
-
A double WAP domain-containing protein Es-DWD1 from Eriocheir sinensis exhibits antimicrobial and proteinase inhibitory activities.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 13;8(8):e73563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073563. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967346 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning, expression, and regulation of goose leptin receptor gene in adipocytes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Jul;353(1-2):267-74. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0795-4. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21445623
-
Transcriptome analysis and discovery of genes involved in immune pathways from hepatopancreas of microbial challenged mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 17;8(7):e68233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068233. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuen BS, Owens PC, Symonds ME, Keisler DH, McFarlane JR, et al. Effects of leptin on fetal plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol concentrations and the timing of parturition in the sheep. Biol Reprod. 2004;70:1650–1657. - PubMed
-
- Paula-Lopes FF, Boelhauve M, Habermann FA, Sinowatz F, Wolf E. Leptin promotes meiotic progression and developmental capacity of bovine oocytes via cumulus cell-independent and -dependent mechanisms. Biol Reprod. 2007;76:532–541. - PubMed
-
- Kronfeld-Schor N, Zhao J, Silvia BA, Bicer E, Mathews PT, et al. Steroid-dependent up-regulation of adipose leptin secretion in vitro during pregnancy in mice. Biol Reprod. 2000;63:274–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

