A report of gastric fundic gland polyps
- PMID: 20567540
- PMCID: PMC2886442
A report of gastric fundic gland polyps
Figures

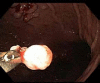
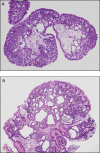
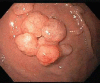
References
-
- Weston BR, Helper DJ, Rex DK. Positive predictive value of endoscopic features deemed typical of gastric fundic gland polyps. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;36:399–402. - PubMed
-
- Burt RW. Gastric fundic gland polyps. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1462–1469. - PubMed
-
- Carmack SW, Genta RM, Schuler CM, Saboorian MH. The current spectrum of gastric polyps: A 1-year national study of over 120,000 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:1524–1532. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi LK, Burke CA, Bennett AE, Lopez R, Hasson H, Church JM. Fundic gland polyp dysplasia is common in familial adenomatous polyposis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:180–185. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
