Classical and Novel Prognostic Markers for Breast Cancer and their Clinical Significance
- PMID: 20567632
- PMCID: PMC2883240
- DOI: 10.4137/cmo.s4773
Classical and Novel Prognostic Markers for Breast Cancer and their Clinical Significance
Abstract
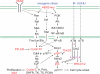
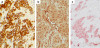
The use of biomarkers ensures breast cancer patients receive optimal treatment. Established biomarkers such as estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) have been playing significant roles in the selection and management of patients for endocrine therapy. HER2 is a strong predictor of response to trastuzumab. Recently, the roles of ER as a negative and HER2 as a positive indicator for chemotherapy have been established. Ki67 has traditionally been recognized as a poor prognostic factor, but recent studies suggest that measurement of Ki67-positive cells during treatment will more effectively predict treatment efficacy for both anti-hormonal and chemotherapy. p53 mutations are found in 20-35% of human breast cancers and are associated with aggressive disease with poor clinical outcome when the DNA-binding domain is mutated. The utility of cyclin D1 as a predictor of breast cancer prognosis is controversial, but cyclin D1b overexpression is associated with poor prognosis. Likewise, overexpression of the low molecular weight form of cyclin E1 protein predicts poor prognosis. Breast cancers from BRCA1/2 carriers often show high nuclear grades, negativity to ER/PR/HER2, and p53 mutations, and thus, are associated with poor prognosis. The prognostic values of other molecular markers, such as p14(ARF), TBX2/3, VEGF in breast cancer are also discussed. Careful evaluation of these biomarkers with current treatment modality is required to determine whether their measurement or monitoring offer significant clinical benefits.
Keywords: ARF; BRCA1/2; ER; HER2; Ki67; PR; TBX2/3; VEGF; breast cancer; cyclin D1; cyclin E; molecular marker; p53; prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Andreopoulou E, Hortobagyi GN. Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Successes and Challenges Toward Individualized Therapy. J Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:3660–2. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49. - PubMed
-
- Masood S. Prognostic/predictive factors in breast cancer. Clin Lab Med. 2005;25:809–25. - PubMed
-
- Morrow PK, Hortobagyi GN. Management of breast cancer in the genome era. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:153–65. - PubMed
-
- Dickson RB, Lippman ME. Autocrine and paracrine growth factors in the normal and neoplastic breast. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Morrow M, et al., editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2000. p. 303.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

