Suture fixation technique for endoscopic brow lift
- PMID: 20567688
- PMCID: PMC2884856
- DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1019142
Suture fixation technique for endoscopic brow lift
Abstract
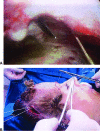
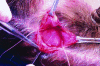
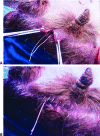
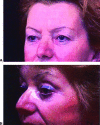
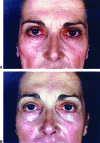
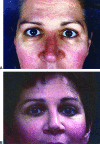
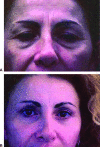
Endoscopic brow lift has become widely accepted as a procedure for restoring a youthful brow, as only three, hardly noticeable incisions of the scalp are needed for this subperiosteal dissection and final repositioning of the brow. It has become an acceptable technique, an alternative to the conventional technique or transcoronal browpexy. Endoscopic brow lift allows separation and repositioning of the periosteum of the orbital rims and zygomaxilla. In a 7-year period beginning September 1999, 350 patients underwent endoscopic brow lift. In these patients, we used our fixation approach, which was accomplished with an absorbable suture subperiosteally. Satisfactory forehead rejuvenation was obtained in all patients with correct eyebrow movement. Long-term results over 7 years confirm the strength and durability of our fixation approach. We consider this approach to be a simple, fast, and reliable fixation technique that establishes precise, secure, and direct brow fixation that allows satisfactory and long-lasting cosmetic results.
Keywords: Suture fixation; endoscopic brow lift.
Figures





Similar articles
-
An alternative fixation technique for the endoscopic brow lift.Ann Plast Surg. 2006 Jun;56(6):599-604. doi: 10.1097/01.sap.0000203317.50871.5c. Ann Plast Surg. 2006. PMID: 16721069
-
Evolution in techniques for endoscopic brow lift with deep temporal fixation only and lower blepharoplasty-transconjunctival fat repositioning.Facial Plast Surg. 2007 Feb;23(1):27-42; discussion 43-4. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-970130. Facial Plast Surg. 2007. PMID: 17330770
-
Experience with cortical tunnel fixation in endoscopic brow lift: the "bevel and slide" modification.Int J Surg. 2009 Dec;7(6):510-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2009.08.013. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Int J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19800433 Review.
-
Biodegradable positive fixation for the endoscopic brow lift.Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996 Nov;98(6):1087-91. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199611000-00027. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996. PMID: 8911483
-
Evolving fixation methods in endoscopically assisted forehead rejuvenation: controversies and rationale.Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997 Nov;100(6):1575-82; discussion 1583-4. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199711000-00032. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997. PMID: 9385975 Review.
Cited by
-
Fixation Techniques Across Endoscopic Brow Lifts: A Scoping Review.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-05114-1. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40804547 Review.
-
Facial reanimation procedures depicted on radiologic imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014 Sep;35(9):1662-6. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3684. Epub 2013 Aug 14. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014. PMID: 23945230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the results of eyebrow lift by combining methods of subcutaneous flap and thread support in patients with droopy eyebrows.Skin Res Technol. 2023 Feb;29(2):e13284. doi: 10.1111/srt.13284. Skin Res Technol. 2023. Retraction in: Skin Res Technol. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70210. doi: 10.1111/srt.70210. PMID: 36823510 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Subcutaneous lateral brow lift ("Z-lift").GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW. 2015 Dec 15;4:Doc16. doi: 10.3205/iprs000075. eCollection 2015. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW. 2015. PMID: 26734537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Core G B, Vasconez L O, Askren C, et al. Coronal face lift with endoscopic techniques. Plas Surg Forum. 1992;15:227.
-
- Isse N G. Endoscopic facial rejuvenation: endoforehead, the functional lift. Case reports. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1994;18:21–29. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez O M. Endoscopic techniques in facial rejuvenation: an overview. Part 1. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1994;18:141–147. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez O M. Endoscopic subperiosteal browlift and facelift. Clin Plast Surg. 1995;22:639–660. - PubMed
-
- Rohrich R J, Beran S J. Evolving fixation methods in endoscopically assisted forehead rejuvenation: controversies and rationale. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100:1575–1582. - PubMed

