Facial contouring surgery for asians
- PMID: 20567722
- PMCID: PMC2884897
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0028-1110098
Facial contouring surgery for asians
Abstract
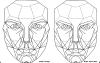
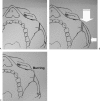
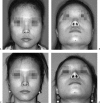
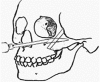
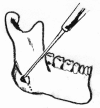
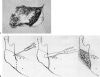
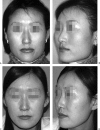
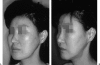
Asian people, especially women, prefer a more delicate and feminine facial shape. To achieve a softer and better facial contour, there are several procedures to change the facial skeleton. Reduction malarplasty and mandibular angleplasty are common facial contouring operations in Asia. A lot of techniques have been developed independently by several authors. Various approaches can be chosen, such as intraoral or external skin incisions. There as also different contouring methods that can be chosen depending on the patient's morphology and the surgeon's technical preferences. The different osteotomy techniques used to mobilize the zygomatic complex can be classified according to the specific portion that is being repositioned. Resection and contouring methods for a prominent mandibular angle can be subdivided according to the specific type of anomaly. The purpose of this article is to review the concepts and various operative procedures for reduction malarplasty and angleplasty. The authors propose a guideline for selecting the appropriate procedure(s) for individual patients. Decisions should be made according to the patient's need, anatomic variations, and possible operative sequelae.
Keywords: Asians; Facial contouring surgery; aesthetic surgery; angleplasty; malarplasty.
Figures
References
-
- Baek S M, Chung Y D, Kim S S. Reduction malarplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;88:53–61. - PubMed
-
- Whitaker L A. Aesthetic augmentation of the malar-midface structures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1987;80:337–346. - PubMed
-
- Powell N B, Riley R W, Laub D R. A new approach to evaluation and surgery of the malar complex. Ann Plast Surg. 1988;20:206–214. - PubMed
-
- Cho B C, Lee J H, Baik B S. Reduction malarplasty using sliding setback osteotomy. J Craniofac Surg. 1998;9:275–279. - PubMed
-
- Hinderer U T. Malar implants for improvement of the facial appearance. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1975;56:157–165. - PubMed

