Local antibiotic therapy in osteomyelitis
- PMID: 20567732
- PMCID: PMC2884906
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0029-1214162
Local antibiotic therapy in osteomyelitis
Abstract
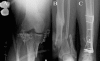
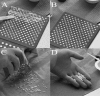
The local delivery of antibiotics in the treatment of osteomyelitis has been used safely and effectively for decades. Multiple methods of drug delivery have been developed for the purposes of both infection treatment and prophylaxis. The mainstay of treatment in this application over the past 20 years has been non-biodegradable polymethylmethacrylate, which has the advantages of excellent elution characteristics and structural support properties. Biodegradable materials such as calcium sulfate and bone graft substitutes have been used more recently for this purpose. Other biodegradable implants, including synthetic polymers, are not yet approved for use but have demonstrated potential in laboratory investigations. Antibiotic-impregnated metal, a recent development, holds great promise in the treatment and prophylaxis of osteomyelitis in the years to come.
Keywords: Antibiotic; biodegradable; elution; methylmethacrylate; osteomyelitis.
Figures

References
-
- Fischer B, Vaudaux P, Magnin M, et al. Novel animal model for studying the molecular mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to bone-implanted metallic devices: role of fibronectin in Staphylococcus aureus adhesion. J Orthop Res. 1996;14:914–920. - PubMed
-
- Adams K, Couch L, Cierny G, Calhoun J, Mader J T. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of antibiotic diffusion from antibiotic-impregnated polymethylmethacrylate beads. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;278:244–252. - PubMed
-
- Nelson C L. The current status of material used for depot delivery of drugs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;427:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Parsons B, Strauss E. Surgical management of chronic osteomyelitis. Am J Surg. 2004;188(Suppl):57–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

