Structural basis for regioisomerization in the alkali-metal-mediated zincation (AMMZn) of trifluoromethyl benzene by isolation of kinetic and thermodynamic intermediates
- PMID: 20568749
- PMCID: PMC3660950
- DOI: 10.1021/ja1038598
Structural basis for regioisomerization in the alkali-metal-mediated zincation (AMMZn) of trifluoromethyl benzene by isolation of kinetic and thermodynamic intermediates
Abstract
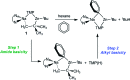
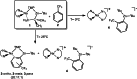
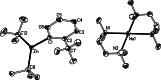
Performed with a desire to advance knowledge of the structures and mechanisms governing alkali-metal-mediated zincation, this study monitors the reaction between the TMP-dialkylzincate reagent [(TMEDA)Na(TMP)((t)Bu)Zn((t)Bu)] 1 and trifluoromethyl benzene C(6)H(5)CF(3) 2. A complicated mixture of products is observed at room temperature. X-ray crystallography has identified two of these products as ortho- and meta-regioisomers of heterotrianionic [(TMEDA)Na(TMP)(C(6)H(4)-CF(3))Zn((t)Bu)], 3-ortho and 3-meta, respectively. Multinuclear NMR data of the bulk crystalline product confirm the presence of these two regioisomers as well as a third isomer, 3-para, in a respective ratio of 20:11:1, and an additional product 4, which also exhibits ortho-zincation of the aryl substrate. Repeating the reaction at 0 degrees C gave exclusively 4, which was crystallographically characterized as [{(TMEDA)(2)Na}(+){Zn(C(6)H(4)-CF(3))((t)Bu)(2)}(-)]. Mimicking the original room-temperature reaction, this kinetic product was subsequently reacted with TMP(H) to afford a complicated mixture of products, including significantly the three regioisomers of 3. Surprisingly, 4 adopts a solvent-separated ion pair arrangement in contrast to the contacted ion variants of 3-ortho and 3-meta. Aided by DFT calculations on model systems, discussion focuses on the different basicities, amido or alkyl, and steps, exhibited in these reactions, and how the structures and bonding within these isolated key metallic intermediates (prior to any electrophilic interception step), specifically the interactions involving the alkali metal, influence the regioselectivity of the Zn-H exchange process.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Meta-metallation of N,N-dimethylaniline: Contrasting direct sodium-mediated zincation with indirect sodiation-dialkylzinc co-complexation.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011;7:1234-48. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.7.144. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 21977208 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic and reactivity studies of hetero-tri-anionic sodium zincates.Dalton Trans. 2016 Apr 14;45(14):6222-33. doi: 10.1039/c5dt04329h. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Dalton Trans. 2016. PMID: 26666657
-
Evaluating cis-2,6-dimethylpiperidide (cis-DMP) as a base component in lithium-mediated zincation chemistry.Chemistry. 2013 Sep 27;19(40):13492-503. doi: 10.1002/chem.201301180. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Chemistry. 2013. PMID: 23955639 Free PMC article.
-
New reactivity and structural insights of alkali-metal-mediated alumination in directed ortho-alumination of a tertiary aromatic amide.Chem Commun (Camb). 2006 Aug 14;(30):3208-10. doi: 10.1039/b606080c. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Chem Commun (Camb). 2006. PMID: 17028745
-
Avant-garde metalating agents: structural basis of alkali-metal-mediated metalation.Acc Chem Res. 2009 Jun 16;42(6):743-55. doi: 10.1021/ar800254y. Acc Chem Res. 2009. PMID: 19348412
Cited by
-
Meta-metallation of N,N-dimethylaniline: Contrasting direct sodium-mediated zincation with indirect sodiation-dialkylzinc co-complexation.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011;7:1234-48. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.7.144. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 21977208 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Selective Copper-Catalyzed Amination and Azidation of Arenes and Heteroarenes via Deprotonative Zincation.J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Aug 23;139(33):11622-11628. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b07661. Epub 2017 Aug 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 28753007 Free PMC article.
-
Main group multiple C-H/N-H bond activation of a diamine and isolation of a molecular dilithium zincate hydride: experimental and DFT evidence for alkali metal-zinc synergistic effects.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Aug 31;133(34):13706-17. doi: 10.1021/ja205547h. Epub 2011 Aug 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21777000 Free PMC article.
-
Arene Activation by Calcium Hydride/Zinc Amide Equilibration.J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Aug 13;147(32):29554-29567. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c10735. Epub 2025 Aug 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 40751684 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-Metal-Trapping Meets Frustrated-Lewis-Pair Chemistry: Ga(CH2SiMe3)3-Induced C-H Functionalizations.Inorg Chem. 2017 Aug 7;56(15):8615-8626. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b00549. Epub 2017 May 9. Inorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 28485929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knochel P.; Leuser H.; Gong L.-Z.; Perrone S.; Kneisel F. F. In Handbook of Functionalised Organometallics; Knochel P., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2005.
-
- The chemistry of organozinc compounds; Rappoport Z., Marek I., Eds.; Patai Series; Wiley: Chichester, U.K., 2006.
-
- Kondo Y.; Shilai M.; Uchiyama M.; Sakamoto T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 3539.
- Uchiyama M. M.; Matsumoto Y.; Nobuto D.; Furuyama T.; Yamaguchi K.; Morokuma K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8748. - PubMed
- Clegg W.; Dale S. H.; Hevia E.; Honeyman G. W.; Mulvey R. E. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2370. - PubMed
-
- Andrikopoulos P. C.; Armstrong D. R.; Barley H. R. L.; Clegg W.; Dale S. H.; Hevia E.; Honeyman G. W.; Kennedy A. R.; Mulvey R. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6184. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

