Addiction research centres and the nurturing of creativity: the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
- PMID: 20569230
- PMCID: PMC3024445
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.02995.x
Addiction research centres and the nurturing of creativity: the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
Abstract
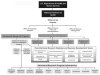
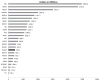
The aim of this paper is to present a concise account of the history, mission, structure and some recent achievements of the US National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). Created by the US Congress 40 years ago, the NIAAA has evolved from an entity charged mainly with building a national system of alcoholism treatment services to one with responsibility for developing, nurturing and supporting the biomedical and behavioral science foundation necessary to reduce the significant domestic and global public health impact of alcohol use disorders. The NIAAA is unique in that it functions both as a funding agency, supporting research at universities and other external, or 'extramural' research institutions, and is also a research institution itself, where alcohol research is carried out in-house, or 'intramurally'. Of a $450.2 million 2009 Congressional Appropriation, approximately 90% was devoted toward the former and approximately 10% towards the latter objective. The current NIAAA Strategic Plan builds on a new organizing principle for long-range research planning, based on a life-span perspective that recognizes that human biology and behavior continue to change throughout life and changes occurring throughout the life-span affect individuals' drinking patterns as well as the decisions they may make to change their drinking habits or to seek help for alcohol use problems. Within this framework, major efforts are currently being devoted to educating practitioners on clinically useful, science-based assessment and treatment methods that exist today, and development of personalized new treatments for tomorrow.
© 2010 The Authors. Journal compilation © 2010 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NIAAA Marks 50 Years of Advancing Alcohol Research.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Dec;44(12):2619-2620. doi: 10.1111/acer.14523. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 33290617 No abstract available.
-
The 40th anniversary of the National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse: the impact on liver disease.Hepatology. 2010 Jul;52(1):10-2. doi: 10.1002/hep.23790. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20578124 No abstract available.
-
Should the reorganization of addiction-related research across all the National Institutes of Health be structural?--The devil is truly in the details.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Apr;35(4):572-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01493.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21443646 Free PMC article.
-
NIAAA: advancing alcohol research for 40 years.Alcohol Res Health. 2010;33(1-2):5-17. Alcohol Res Health. 2010. PMID: 23579932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on the neuroscience of alcohol from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;125:15-29. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-62619-6.00002-1. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25307566 Review.
References
-
- Comprehensive Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Prevention. Treatment, and Rehabilitation Act of 1970, Pub. L. no. 91–616. 1970.
-
- Blocker JS, Fahey DM, Tyrell IR. Alcohol and Temperance in Modern History: An International Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO; 2003. p. 437.
-
- Hughes HE. Foreword. Alcohol Health Res World. 1988;12:234–5.
-
- Gordis E. Reports from research centres—12. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Br J Addict. 1988;83:483–93. - PubMed
-
- George DT, Gilman J, Hersh J, Thorsell A, Herion D, Geyer C, et al. Neurokinin 1 receptor antagonism as a possible therapy for alcoholism. Science. 2008;319:1536–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

