Duplex real-time reverse transcriptase PCR to determine cytokine mRNA expression in a hamster model of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis
- PMID: 20569429
- PMCID: PMC2909172
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-31
Duplex real-time reverse transcriptase PCR to determine cytokine mRNA expression in a hamster model of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis
Abstract
Background: The Syrian hamster, Mesocricetus auratus, has distinct immunological features and is uniquely susceptible to intracellular pathogens. Studies in hamsters are limited by the relative unavailability of tools to conduct immunological studies. To address this limitation we developed duplex real-time reverse transcriptase (RT) PCR assays for the relative quantification of the mRNAs of hamster cytokines, chemokines, and related immune response molecules.
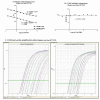
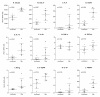
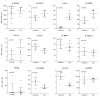
Results: Real-time RT-PCR primers and probes were synthesized for analysis of interleukin (IL)-4, IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, IL-10, IL-12p40, TGF-beta, IL-13, IL-21, chemokine ligand (CCL) 22, CCL17, Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 4 and FoxP3 expression. Standard curves and validation experiments were performed for each real-time RT-PCR assay, allowing us to use the comparative Ct (2-DeltaDeltaCt) method to calculate changes in gene expression. Application of the real-time RT PCR assays to a biological model was demonstrated by comparing mRNA expression in skin and lymph node tissues between uninfected and Leishmania panamensis infected hamsters.
Conclusions: The duplex real-time RT PCR assays provide a powerful approach for the quantification of cytokine transcription in hamsters, and their application to a model of cutaneous leishmaniasis suggests that a balanced type 1 and type 2 cytokine response contributes to the chronic, nonprogressive course of disease. These new molecular tools will further facilitate investigation into the mechanisms of disease in the hamster, not only for models of leishmaniasis, but also for other viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections.
Figures
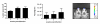
References
-
- Hommel M, Jaffe CL, Travi B, Milon G. Experimental models for leishmaniasis and for testing anti-leishmanial vaccines. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1995;89(Suppl 1):55–73. - PubMed
-
- Melby PC, Chandrasekar B, Zhao W, Coe JE. The hamster as a model of human visceral leishmaniasis: progressive disease and impaired generation of nitric oxide in the face of a prominent Th1-like response. J Immunol. 2001;166:1912–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

