Altered blood glucose concentration is associated with risk of death among patients with community-acquired Gram-negative rod bacteremia
- PMID: 20569435
- PMCID: PMC2912309
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-181
Altered blood glucose concentration is associated with risk of death among patients with community-acquired Gram-negative rod bacteremia
Abstract
Background: Altered blood glucose concentration is commonly observed in patients with sepsis, even among those without hypoglycemic treatments or history of diabetes mellitus. These alterations in blood glucose are potentially detrimental, although the precise relationship with outcome in patients with bacteremia has not been yet determined.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study design for analyzing patients with Gram negative rod bacteremia was employed, with the main outcome measure being in-hospital mortality. Patients were stratified in quintiles accordingly deviation of the blood glucose concentration from a central value with lowest mortality. Cox proportional-hazards regression model was used for determining the relationship of same day of bacteremia blood glucose and death.
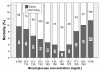
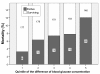
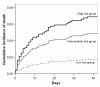
Results: Of 869 patients identified 63 (7.4%) died. Same day of bacteremia blood glucose concentration had a U-shaped relationship with in-hospital mortality. The lowest mortality (2%) was detected in the range of blood glucose concentration from 150 to 160 mg/dL. Greater deviation of blood glucose concentration from the central value of this range (155 mg/dL, reference value) was directly associated with higher risk of death (p = 0.002, chi for trend). The low-risk group (quintile 1) had a mortality of 3.3%, intermediate-risk group (quintiles 2, 3 and 4) a mortality of 7.1%, and the high-risk group (quintile 5) a mortality of 12.05%. In a multivariable Cox regression model, the hazard ratio for death among patients in the intermediate-risk group as compared with that in the low risk group was 2.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.01 to 8.18; P = 0.048), and for the high risk group it was 4.26 (95% confidence interval, 1.41 to 12.94; P = 0.01).
Conclusions: Same day of bacteremia blood glucose concentration is related with outcome of patients with Gram-negative rod bacteremia. Lowest mortality is detected in patients with blood glucose concentration in an interval of 150-160 mg/dL. Deviations from these values are associated with an increased risk of death.
Figures
References
-
- Weinstein MP, Towns ML, Quartey SM, Mirrett S, Reimer LG, Parmigiani G, Reller LB. The clinical significance of positive blood cultures in the 1990s: a prospective comprehensive evaluation of the microbiology, epidemiology, and outcome of bacteremia and fungemia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;24:584–602. - PubMed
-
- Shilo S, Berezovsky S, Friedlander Y, Sonnenblick M. Hypoglycemia in hospitalized nondiabetic older patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998;46:978–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

