Hsa-miR-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p are downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and have inverse effects on invasion and migration of lung cancer cells
- PMID: 20569443
- PMCID: PMC2903529
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-318
Hsa-miR-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p are downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and have inverse effects on invasion and migration of lung cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Two mature microRNAs (miRNAs), hsa-miR-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p (collectively referred to as hsa-miR-125a-3p/5p), are derived from 3' and 5' ends of pre-miR-125a, respectively. Although impaired regulation of hsa-miR-125a-5p has been observed in some tumors, the role of this miRNA in invasion and metastasis remains unclear, and few studies have examined the function of hsa-miR-125a-3p. In order to characterize the functions of hsa-miR-125a-3p/5p in invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), we investigated the relationships between hsa-miR-125a-3p/5p expression and lymph node metastasis in NSCLC tissues. We also explored the impact of expression of these miRNAs on invasive and migratory capabilities of lung cancer cells.
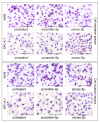
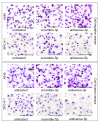
Methods: Expression of hsa-miR-125a-3p/5p in NSCLC tissues was explored using real-time PCR. The relationships between hsa-miR-125a-3p/5p expression and pathological stage or lymph node metastasis were assessed using the Spearman correlation test. For in vitro studies, lung cancer cells were transfected with sense and antisense 2'-O-methyl oligonucleotides for gain-of-function and loss-of-function experiments. Transwell experiments were performed to evaluate cellular migration and invasion.
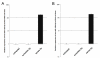
Results: Expression of hsa-miR-125a-3p/5p was lower in NSCLC tissues than in adjacent normal lung tissues (LAC). Furthermore, the results from the Spearman correlation test showed a negative relationship between hsa-miR-125a-3p expression and pathological stage or lymph node metastasis and an inverse relationship between hsa-miR-125a-5p expression and pathological stage or lymph node metastasis. In vitro gain-of-function experiments indicated that hsa-miR-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p function in an opposing manner, suppressing or enhancing cell migration and invasion in A549 and SPC-A-1 cell lines, respectively. These opposing functions were further validated by suppression of hsa-miR-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p expression in loss-of-function experiments.
Conclusion: Hsa-miR-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p play distinct roles in regulation of invasive and metastatic capabilities of lung cancer cells, consistent with the opposing correlations between the expression of these miRNAs and lymph node metastasis in NSCLC. These results provide new insights into the roles of miR-125a family members in the development of NSCLC.
Figures
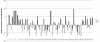
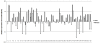
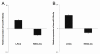

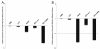
References
-
- Grishok A, Pasquinelli AE, Conte D, Li N, Parrish S, Ha I, Baillie DL, Fire A, Ruvkun G, Mello CC. Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell. 2001;106:23–34. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00431-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

