Characterization of a diverse secretome generated by the mouse preimplantation embryo in vitro
- PMID: 20569467
- PMCID: PMC2900276
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-8-71
Characterization of a diverse secretome generated by the mouse preimplantation embryo in vitro
Abstract
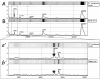
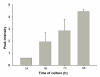
This study investigates the suitability of surface-enhanced laser desorption and ionization time-of-flight (SELDI-TOF) and electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry for analysis of the proteins released by the mouse preimplantation embryo in vitro. SELDI-TOF analysis with CM10 or IMAC30 (but not Q10) protein chips detected a protein peak at m/z approximately 8570 released by both C57BL6 and hybrid embryos. No other peaks unique to the presence of the embryo were identified with this method. ESI mass spectrometry of tryptic digests of embryo-conditioned media identified a total of 20 proteins released during development from the zygote to blastocyst stage. Four proteins were expressed in at least 7 out of 8 cultures tested, one of these (lactate dehydrogenase B) was in all cultures. A further five proteins were in at least half of the cultures and 11 more proteins were in at least one culture. The expression of two of these proteins is essential for preimplantation embryo development (NLR family, pyrin domain containing 5 and peptidyl arginine deiminase, type VI). A further four proteins detected have roles in redox regulation of cells, and three others are capable of inducing post-translational modifications of proteins. This study shows the feasibility of ESI mass spectrometry for identifying the proteins secreted by the preimplantation embryo in vitro. This analysis identifies a range of targets that now require detailed functional analysis to assess whether their release by the embryo is an important property of early embryo development.
Figures

References
-
- Wells XE, O'Neill C. Biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor by the mouse two-embryo. J Reprod Fertil. 1992;96:61–71. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill C. Partial characterisation of the embryo-derived platelet activating factor in mice. J Reprod Fertil. 1985;75:375–380. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill C, Gidley-Baird AA, Pike IL, Saunders DM. Use of a bio-assay for embryo-derived platelet activating factor as a means of assessing quality and pregnancy potential of human embryos. Fertil Steril. 1987;47:969–975. - PubMed
-
- Punjabi U, Vereeken A, Delbeke L, Angle M, Gieles M, Gerris J, Johnston J, Buytaert PP. Embryo-derived platelet-activating factor, a marker of embryo quality and viability following ovarian stimulation for invitro fertilization. J in Vitro Fert Emb Transf. 1990;7(6):321–326. doi: 10.1007/BF01130583. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

