Endovascular treatment of incoercible epistaxis and epidural cerebral hematoma. A case report
- PMID: 20569576
- PMCID: PMC3354540
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990601200305
Endovascular treatment of incoercible epistaxis and epidural cerebral hematoma. A case report
Abstract
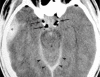
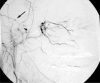
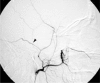
A young patient with a facial trauma after a road accident was admitted to our department with incoercible epistaxis. A CT scan showed a right pterional acute epidural hematoma (EDH). Angiography demonstrated multiple sources of bleeding of the right sphenopalatine arteries, cause of the epistaxis, and an intracranial leakage of the right middle meningeal artery, responsible for the EDH. The patient immediately underwent embolization of the right internal maxillary artery and right middle meningeal artery. The procedure stopped the epistaxis and no further enlargement of the EDH was observed, avoiding its surgical treatment. Endovascular surgery may be an effective procedure to stop the arterial meningeal bleeding sustaining acute EDH and may be a useful tool in the management of special cases of post traumatic EDH.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Traumatic epidural hematoma treated with endovascular coil embolization.Surg Neurol Int. 2021 Jul 6;12:322. doi: 10.25259/SNI_939_2020. eCollection 2021. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 34345463 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular management of acute epidural hematomas: clinical experience with 80 cases.J Neurosurg. 2018 Apr;128(4):1044-1050. doi: 10.3171/2016.11.JNS161398. Epub 2017 Apr 14. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28409733
-
Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for the Treatment of an Expanding Epidural Hematoma.World Neurosurg. 2019 Aug;128:284-286. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.05.084. Epub 2019 May 17. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31108255
-
Chronic Epidural Hematoma Caused by Traumatic Intracranial Pseudoaneurysm of the Middle Meningeal Artery: Review of the Literature with a Focus on this Unique Entity.World Neurosurg. 2020 Apr;136:198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.12.179. Epub 2020 Jan 9. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31927123 Review.
-
Development of a delayed acute epidural hematoma following contralateral epidural hematoma evacuation: case report and review of literature.Acta Neurol Belg. 2019 Mar;119(1):15-20. doi: 10.1007/s13760-018-1049-y. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Acta Neurol Belg. 2019. PMID: 30478538 Review.
Cited by
-
Traumatic epidural hematoma treated with endovascular coil embolization.Surg Neurol Int. 2021 Jul 6;12:322. doi: 10.25259/SNI_939_2020. eCollection 2021. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 34345463 Free PMC article.
-
Middle meningeal artery embolization to treat progressive epidural hematoma: a case report.J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2020 Mar;22(1):20-25. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2020.22.1.20. Epub 2020 Mar 31. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32596140 Free PMC article.
-
Variability of the Middle Meningeal Artery Subject to the Shape of Skull.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2015 Dec;76(6):451-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1554902. Epub 2015 Jun 12. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2015. PMID: 26682123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bejjani GK, Donahue DJ, Rusin J. Radiological and clinical criteria for the management of epidural hematomas in children. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1996;25:302–308. - PubMed
-
- Bezircioglu H, Ersahin Y, et al. Nonoperative treatment of acute extradural hematomas: analysis of 80 cases. J Trauma. 1996;41:696–698. - PubMed
-
- Bricolo AP, Pasut LM. Extradural hematoma: toward zero mortality. Neurosurgery. 1984;14:8–12. - PubMed
-
- Bullock R, Smith RM, Dellen JR. Non-operative management of extradural hematoma. Neurosurgery. 1985;16:602–605. - PubMed
-
- Chen TY, Wong CW, et al. The expectant treatment of "asymptomatic" supratentorial epidural hematomas. Neurosurgery. 1993;32:176–179. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

