Evaluation of the Stability of Small Ruptured Aneurysms with a Small Neck after Embolization with Guglielmi Detachable Coils. Correlation between Coil Packing Ratio and Coil Compaction
- PMID: 20569609
- PMCID: PMC3387974
- DOI: 10.1177/15910199060120S113
Evaluation of the Stability of Small Ruptured Aneurysms with a Small Neck after Embolization with Guglielmi Detachable Coils. Correlation between Coil Packing Ratio and Coil Compaction
Abstract
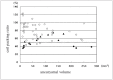
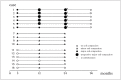
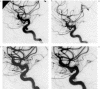
It is difficult to predict the compaction of Guglielmi detachable coils (GDC) after endovascular surgery for aneurysms. Therefore, we studied the relationship between the coil packing ratio and compaction in 62 patients with acute ruptured intracranial aneurysms that were small (< 10 mm) had a small neck (< 4 mm) and were coil-embolized with GDC-10. We recorded the maximum prospective coil length, L, as the length that correspond with the volume of packed coils occupying 30% of the aneurysmal volume. L was calculated as L (cm) = 0.3 x a x b x c and the coil packing ratio expressed as packed coil length/L x 100, where a, b, and c are the aneurysmal height, length, and width in mm, respectively. Angiographic followup studies were performed at three months and one and two years after endovascular surgery. Of the 62 patients, 16 (25.8%) manifested angiographic coil compaction (ten minor and six major compactions); the mean coil packing ratio was 51.9 +/- 13.4%. The mean coil packing ratio in the other 46 patients was 80.5 +/- 20.2% and the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.01). In all six patients with major compaction the mean packing ratio was below 50%. We detected 93.8% of the compactions within 24 months of coil placement. In patients with small, necked aneurysms, the optimal coil packing ratio could be identified with the formula 0.3 x a x b x c. The probability of compaction was significantly higher when the coil packing ratio was under 50%. To detect coil compaction post-embolization, follow-up angiograms must be examined regularly for at least 24 months.
Figures

References
-
- Bavinzski G, Richling B, et al. Endosaccular occlusion of basilar artery bifurcation aneurysms using electrically detachable coils. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1995;134:184–189. - PubMed
-
- Redekop GJ, Durity FA, et al. Management-related morbidity in unselected aneurysms of the upper basilar artery. J Neurosurg. 1997;87:836–842. - PubMed
-
- Uda K, Goto K, et al. Embolization of cerebral aneurysms using Guglielmi detachable coils - problems and treatment plans in the acute stage after subarachnoid haemorrhage and long-term efficiency. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1998;38:143–152. - PubMed
-
- Satoh K, Matsubara S, et al. Intracranial aneurysm embolization using interlocking detachable coils. Interventional Neuroradiology. 1997;3(Suppl 2):125–128. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

