Epigenetic regulation of stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila testis via the nucleosome-remodeling factor NURF
- PMID: 20569693
- PMCID: PMC2897240
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.04.018
Epigenetic regulation of stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila testis via the nucleosome-remodeling factor NURF
Abstract
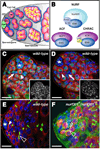
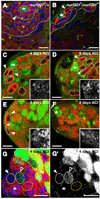
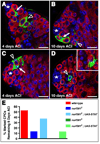
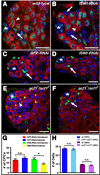
Regulation of stem cells depends on both tissue-specific transcriptional regulators and changes in chromatin organization, yet the coordination of these events in endogenous niches is poorly understood. In the Drosophila testis, local JAK-STAT signaling maintains germline and somatic stem cells (GSCs and cyst progenitor cells, or CPCs) in a single niche. Here we show that epigenetic regulation via the nucleosome-remodeling factor (NURF) complex ensures GSC and CPC maintenance by positively regulating JAK-STAT signaling, thereby preventing premature differentiation. Conversely, NURF is not required in early differentiating daughter cells of either lineage. Because three additional ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers (ACF, CHRAC, and dMi-2/NuRD) are dispensable for stem cell maintenance in the testis, epigenetic regulation of stem cells within this niche may rely primarily on NURF. Thus, local signals cooperate with specific chromatin-remodeling complexes in intact niches to coordinately regulate a common set of target genes to prevent premature stem cell differentiation.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Arbouzova NI, Bach EA, Zeidler MP. Ken & barbie selectively regulates the expression of a subset of Jak/STAT pathway target genes. Curr Biol. 2006;16:80–88. - PubMed
-
- Arney KL, Fisher AG. Epigenetic aspects of differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:4355–4363. - PubMed
-
- Becker PB, Horz W. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:247–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

