Diagnosis and management of clinical chorioamnionitis
- PMID: 20569811
- PMCID: PMC3008318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2010.02.003
Diagnosis and management of clinical chorioamnionitis
Abstract
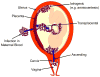
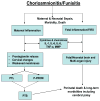
Chorioamnionitis is a common complication of pregnancy associated with significant maternal, perinatal, and long-term adverse outcomes. Adverse maternal outcomes include postpartum infections and sepsis whereas adverse infant outcomes include stillbirth, premature birth, neonatal sepsis, chronic lung disease, and brain injury leading to cerebral palsy and other neurodevelopmental disabilities. Research in the past 2 decades has expanded understanding of the mechanistic links between intra-amniotic infection and preterm delivery as well as morbidities of preterm and term infants. Recent and ongoing clinical research into better methods for diagnosing, treating, and preventing chorioamnionitis is likely to have a substantial impact on short and long-term outcomes in the neonate.
Figures
References
-
- Eschenbach DA. Ureaplasma urealyticum and premature birth. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17 (Suppl 1):S100–6. - PubMed
-
- Gibbs RS, Duff P. Progress in pathogenesis and management of clinical intraamniotic infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991;164:1317. - PubMed
-
- Soper DE, Mayhall CG, Dalton HP. Risk factors for intraamniotic infection: a prospective epidemiologic study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989;161:562. - PubMed
-
- Newton ER. Chorioamnionitis and intraamniotic infection. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1993;36:795. - PubMed
-
- Newton ER, Prihoda TJ, Gibbs RS. Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for intra-amniotic infection. Obstet Gynecol. 1989;73:571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous