Group B streptococcal disease in infants: progress in prevention and continued challenges
- PMID: 20569813
- PMCID: PMC11848810
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2010.02.002
Group B streptococcal disease in infants: progress in prevention and continued challenges
Abstract
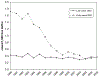
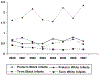
The burden of early-onset disease caused by group B Streptococcus (GBS) has decreased dramatically in the United States over the past 20 years. Universal culture-based screening at 35 to 37 weeks gestational age and use of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis are the cornerstones of prevention measures that have led to this decline. GBS, however, remains the leading cause of early-onset neonatal sepsis in the United States. Revised guidelines for prevention of perinatal GBS are planned for issuance in 2010. This article discusses implementation challenges for clinicians caring for pregnant women and newborns and presents an updated algorithm for neonatal management.
Figures
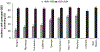

References
-
- Baker CJ, Barrett FF, Gordon RC, et al. Suppurative meningitis due to streptococci of Lancefield group B: a study of 33 infants. J Pediatr 1973;82(4):724–9. - PubMed
-
- Barton LL, Feigin RD, Lins R. Group B beta hemolytic streptococcal meningitis in infants. J Pediatr 1973;82(4):719–23. - PubMed
-
- Franciosi RA, Knostman JD, Zimmerman RA. Group B streptococcal neonatal and infant infections. J Pediatr 1973;82(4):707–18. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Trends in perinatal group B streptococcal disease—United States, 2000–2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2009;58(5):109–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

