Comparative histopathology and immunohistochemistry of QX-like, Massachusetts and 793/B serotypes of infectious bronchitis virus infection in chickens
- PMID: 20570279
- PMCID: PMC7127812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2010.04.007
Comparative histopathology and immunohistochemistry of QX-like, Massachusetts and 793/B serotypes of infectious bronchitis virus infection in chickens
Abstract
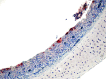
The aim of this study was to compare experimentally the pathogenicity and tissue distribution of the recently emerged QX-like strain of infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) with the widespread M41 and 793/B serotypes of the virus. Histopathological and immunohistochemical methods were employed to define the main sites of virus replication. One-day-old specific pathogen free chickens were inoculated with five different QX-like strains, or with the M41 and 793/B IBV strains and monitored for 42 days post-infection. Tracheal lesions developed in all infected birds, confirming the ability of all of the tested strains to induce respiratory disease. Replication of the isolates in the alimentary tract was detected, but the infection did not cause significant gut lesions. Four of the five QX-like IBV strains induced severe kidney lesions. Dilation of the oviduct with accumulation of serum-like fluid in the lumen of this structure, reported previously from field cases of QX-like IBV infection, was observed following experimental infection with all of the five QX-like strains. Microscopical and immunohistochemical examination of the affected oviducts did not help to elucidate the pathogenesis of this lesion.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of the pathogenicity of QX-like, M41 and 793/B infectious bronchitis strains from different pathological conditions.Avian Pathol. 2009 Dec;38(6):449-56. doi: 10.1080/03079450903349196. Avian Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19937534
-
Induction of cystic oviducts and protection against early challenge with infectious bronchitis virus serotype D388 (genotype QX) by maternally derived antibodies and by early vaccination.Avian Pathol. 2011 Oct;40(5):463-71. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2011.599060. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Avian Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21834621
-
Pathogenicity differences between QX-like and Mass-type infectious bronchitis viruses.Vet Microbiol. 2018 Jan;213:129-135. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.11.027. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Vet Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29291996
-
Global distributions and strain diversity of avian infectious bronchitis virus: a review.Anim Health Res Rev. 2017 Jun;18(1):70-83. doi: 10.1017/S1466252317000044. Anim Health Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28776490 Review.
-
Avian infectious bronchitis virus.Rev Sci Tech. 2000 Aug;19(2):493-508. doi: 10.20506/rst.19.2.1228. Rev Sci Tech. 2000. PMID: 10935276 Review.
Cited by
-
Two novel neutralizing antigenic epitopes of the s1 subunit protein of a QX-like avian infectious bronchitis virus strain Sczy3 as revealed using a phage display peptide library.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2015 Nov 15;168(1-2):49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 26315775 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple recombination events between field and vaccine strains resulted in the emergence of a novel infectious bronchitis virus with decreased pathogenicity and altered replication capacity.Poult Sci. 2020 Apr;99(4):1928-1938. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.11.056. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32241473 Free PMC article.
-
Phylodynamic and Recombination Analyses of Avian Infectious Bronchitis GI-23 Reveal a Widespread Recombinant Cluster and New Among-Countries Linkages.Animals (Basel). 2021 Nov 8;11(11):3182. doi: 10.3390/ani11113182. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827914 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological assessment and tissue tropism of two different Egyptian infectious bronchitis strains.Virusdisease. 2023 Sep;34(3):410-420. doi: 10.1007/s13337-023-00842-x. Epub 2023 Sep 17. Virusdisease. 2023. PMID: 37780904 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus Infection in Chickens: Multiple System Disease with Immune Suppression.Pathogens. 2020 Sep 24;9(10):779. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9100779. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32987684 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambali A.G., Jones R.C. Early pathogenesis in chicks of infection with an enterotropic strain of infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Diseases. 1990;34:809–817. - PubMed
-
- Beato M.S., De Battisti C., Terregino C., Drago A., Capua I. Evidence of circulation of a Chinese strain of infectious bronchitis virus (QXIBV) in Italy. Veterinary Record. 2005;156:720. - PubMed
-
- Benyeda Z., Mató T., Süveges T., Szabó É, Kardi V. Comparison of the pathogenicity of QX-like, M41 and 793/B infectious bronchitis strains from different pathological conditions. Avian Pathology. 2009;38:449–456. - PubMed
-
- Bochkov Y.A., Batchenko G.V., Shcherbakova L.O., Borisov A.V., Drygin V.V. Molecular epizootiology of avian infectious bronchitis virus in Russia. Avian Pathology. 2006;35:379–393. - PubMed
-
- Boltz D.A., Nakai M., Bahr J.M. Avian infectious bronchitis virus: a possible cause of reduced fertility in the rooster. Avian Diseases. 2004;48:909–915. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

