A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia
- PMID: 20570423
- PMCID: PMC4028168
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.03.014
A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia
Abstract
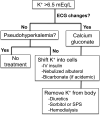
Hyperkalemia is a common and potentially lethal disorder. Given its variable presentation, clinicians should have a high index of suspicion, especially in patients with chronic kidney disease. The present case highlights key physiologic mechanisms in the development of hyperkalemia and provides an outline for emergent treatment. In this context, we discuss specific mechanisms of action of available treatments of hyperkalemia.
Copyright (c) 2010 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Palmer BF. A Physiologic-Based Approach to the Evaluation of a Patient With Hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010 [published online ahead of print ****** doi:****** - PubMed
-
- Schaefer TJ, Wolford RW. Disorders of potassium. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2005;23(3):723–747. - PubMed
-
- Rose BD, Post TW. Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and electrolyte disorders. th edition McGraw-Hill; New York: 2001.
-
- Bia MJ, Lu D, Tyler K, De Fronzo RA. Beta adrenergic control of extrarenal potassium disposal: A beta-2 mediated phenomenon. Nephron. 1986;43(2):117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

