Intact indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in human chronic granulomatous disease
- PMID: 20570568
- PMCID: PMC2946558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2010.05.007
Intact indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in human chronic granulomatous disease
Abstract
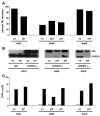
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is characterized by a disability to produce reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI) caused by a defect of phagocyte nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase. A hyperinflammatory response to immune activation has been reported to contribute to the pathology of CGD. The tryptophan catabolizing enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is considered critical for regulating immune responses and suppression of inflammation. IDO is generally believed to require ROI for enzymatic activity and was found to be inactive in murine CGD. Here, we report that, strikingly, in human CGD IDO metabolic activity is intact. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells generated from CGD patients, harbouring X-linked and autosomal recessive forms of CGD, and from healthy controls produced similar amounts of the tryptophan metabolite kynurenine upon activation with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ. Thus, in humans, ROI apparently are dispensable for IDO activity. Hyperinflammation in human CGD cannot be attributed to disabled IDO activation.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Stasia M.J., Li X.J. Genetics and immunopathology of chronic granulomatous disease. Semin Immunopathol. 2008;30:209–235. - PubMed
-
- Bylund J., MacDonald K.L., Brown K.L., Mydel P., Collins L.V., Hancock R.E., Speert D.P. Enhanced inflammatory responses of chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes involve ROS-independent activation of NF-kappa B. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:1087–1096. - PubMed
-
- F.L. van de Veerdonk, S.P. Smeekens, L.A. Joosten, B.J. Kullberg, C.A. Dinarello, J.W. van der Meer, and M.G. Netea, Reactive oxygen species-independent activation of the IL-1beta inflammasome in cells from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107 3030-3033. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marks D.J., Miyagi K., Rahman F.Z., Novelli M., Bloom S.L., Segal A.W. Inflammatory bowel disease in CGD reproduces the clinicopathological features of Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:117–124. - PubMed
-
- Grohmann U., Fallarino F., Puccetti P. Tolerance, DCs and tryptophan: much ado about IDO. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:242–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

