Location-specific activation of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus by localized inflammation
- PMID: 20570615
- PMCID: PMC2939270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.05.007
Location-specific activation of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus by localized inflammation
Abstract
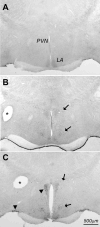
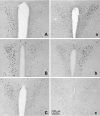
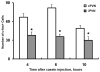
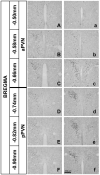
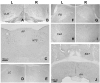
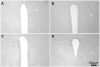
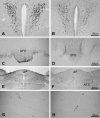
The existence of an immunological homunculus has been proposed, but evidence for location-specific response of the central nervous system to immunological stimulation is lacking. In this study, we show that inflammation induced by injection of casein into one of the causes c-fos expression in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) in an asymmetrical manner: much stronger activation is always induced in the contralateral PVN. Unilateral sciatic nerve transection abolished the casein-induced PVN activation if casein was injected into the hindlimb with the nerve transection, but had no effect if casein was injected into the hindlimb with intact nerve innervation. Injection of casein into one the forelimbs also caused contralateral PNV activation. Further, stronger PVN activation was found in the anterior PVN after the forelimb injection, but in the posterior PVN after the hindlimb injection. Casein-induced PVN activation is absent in IL-1R1 KO, IL-6 KO, TNFα KO, and in C3H/HeJ (TLR4 mutant) animals. In comparison, injection of LPS, a systemic inflammagen, into one hindlimb induced bilateral PVN activation but injection of live Escherichia coli into one hindlimb induced contralateral PVN activation. These results support the notion that local inflammation may activate the PVN by neural routes in a location-specific manner.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 is a needed proinflammatory cytokine in the prolonged neural activity and transcriptional activation of corticotropin-releasing factor during endotoxemia.Endocrinology. 1999 Sep;140(9):3890-903. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.9.6983. Endocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10465257
-
Effect of dexfenfluramine on the transcriptional activation of CRF and its type 1 receptor within the paraventricular nucleus of the rat hypothalamus.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Mar;117(6):1021-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb16692.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8882592 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and interleukin-1 beta-induced activation of c-fos, NGFI-B and CRF gene expression in the hypothalamic PVN: comparison between Sprague-Dawley, Fisher-344 and Lewis rats.J Neuroendocrinol. 1994 Feb;6(1):101-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.1994.tb00559.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 1994. PMID: 8025563
-
Acute glucocorticoid pretreatment suppresses stress-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormone secretion and expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone hnRNA but does not affect c-fos mRNA or fos protein expression in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus.J Neuroendocrinol. 2003 Nov;15(11):1075-83. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2003.01100.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2003. PMID: 14622438
-
Central administration of glucagon-like peptide-1 activates hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons in the rat.Endocrinology. 1997 Oct;138(10):4445-55. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.10.5270. Endocrinology. 1997. PMID: 9322962
Cited by
-
Differential Thermoregulatory and Inflammatory Patterns in the Circadian Response to LPS-Induced Septic Shock.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 12;10:100. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00100. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32226779 Free PMC article.
-
In-depth conversation: spectrum and kinetics of neuroimmune afferent pathways.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Aug;40:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24566385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation plays a causal role in fatigue-like behavior induced by pelvic irradiation in mice.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021 May 19;15:100264. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100264. eCollection 2021 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021. PMID: 34589770 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-induced fever is mediated by IL-6 receptors on brain endothelial cells coupled to STAT3-dependent induction of brain endothelial prostaglandin synthesis.J Neurosci. 2014 Nov 26;34(48):15957-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3520-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25429137 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoception: Defining brain-regulated immunity.Neuron. 2022 Nov 2;110(21):3425-3428. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.016. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 36327893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaishi T, Robbins A, Sakuma Y, Sato Y. Neural inputs from the uterus to the paraventricular magnocellular neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1988;84:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Bester H, Matsumoto N, Besson JM, Bernard JF. Further evidence for the involvement of the spinoparabrachial pathway in nociceptive processes: a c-Fos study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1997;383:439–458. - PubMed
-
- Bomholt SF, Mikkelsen JD, Blackburn-Munro G. Normal hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis function in a rat model of peripheral neuropathic pain. Brain Res. 2005;1044:216–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

