Characterization of a novel MK3 splice variant from murine ventricular myocardium
- PMID: 20570725
- PMCID: PMC5300773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.05.019
Characterization of a novel MK3 splice variant from murine ventricular myocardium
Abstract
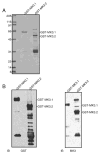
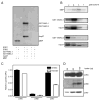
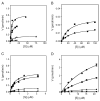
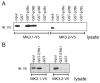
p38 MAP kinase (MAPK) isoforms alpha, beta, and gamma, are expressed in the heart. p38alpha appears pro-apoptotic whereas p38beta is pro-hypertrophic. The mechanisms mediating these divergent effects are unknown; hence elucidating the downstream signaling of p38 should further our understanding. Downstream effectors include MAPK-activated protein kinase (MK)-3, which is expressed in many tissues including skeletal muscles and heart. We cloned full-length MK3 (MK3.1, 384 aa) and a novel splice variant (MK3.2, 266 aa) from murine heart. For MK3.2, skipping of exons 8 and 9 resulted in a frame-shift in translation of the first 85 base pairs of exon 10 followed by an in-frame stop codon. Of 3 putative phosphorylation sites for p38 MAPK, only Thr-203 remained functional in MK3.2. In addition, MK3.2 lacked nuclear localization and export signals. Quantitative real-time PCR confirmed the presence of these mRNA species in heart and skeletal muscle; however, the relative abundance of MK3.2 differed. Furthermore, whereas total MK3 mRNA was increased, the relative abundance of MK3.2 mRNA decreased in MK2(-/-) mice. Immunoblotting revealed 2 bands of MK3 immunoreactivity in ventricular lysates. Ectopically expressed MK3.1 localized to the nucleus whereas MK3.2 was distributed throughout the cell; however, whereas MK3.1 translocated to the cytoplasm in response to osmotic stress, MK3.2 was degraded. The p38alpha/beta inhibitor SB203580 prevented the degradation of MK3.2. Furthermore, replacing Thr-203 with alanine prevented the loss of MK3.2 following osmotic stress, as did pretreatment with the proteosome inhibitor MG132. In vitro, GST-MK3.1 was strongly phosphorylated by p38alpha and p38beta, but a poor substrate for p38delta and p38gamma. GST-MK3.2 was poorly phosphorylated by p38alpha and p38beta and not phosphorylated by p38delta and p38gamma. Hence, differential regulation of MKs may, in part, explain diverse downstream effects mediated by p38 signaling.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

