Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1act/tubulin interaction is an important determinant of mitotic stability in cultured HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells
- PMID: 20570892
- PMCID: PMC2938962
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4490
Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1act/tubulin interaction is an important determinant of mitotic stability in cultured HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells
Abstract
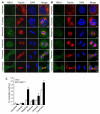
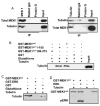
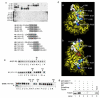
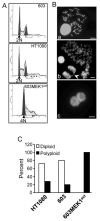
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway plays a major role in neoplastic cell transformation. Using a proteomics approach, we identified alpha tubulin and beta tubulin as proteins that interact with activated MAP/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1 (MEK1), a central MAPK regulatory kinase. Confocal analysis revealed spatiotemporal control of MEK1-tubulin colocalization that was most prominent in the mitotic spindle apparatus in variant HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells. Peptide arrays identified the critical role of positively charged amino acids R108, R113, R160, and K157 on the surface of MEK1 for tubulin interaction. Overexpression of activated MEK1 caused defects in spindle arrangement, chromosome segregation, and ploidy. In contrast, chromosome polyploidy was reduced in the presence of an activated MEK1 mutant (R108A, R113A) that disrupted interactions with tubulin. Our findings indicate the importance of signaling by activated MEK1-tubulin in spindle organization and chromosomal instability.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures


References
-
- Giroux S, Tremblay M, Bernard D, et al. Embryonic death of Mek1-deficient mice reveals a role for this kinase in angiogenesis in the labyrinthine region of the placenta. Curr Biol. 1999;9:369–72. - PubMed
-
- Roovers K, Assoian RK. Integrating the MAP kinase signal into the G1 phase cell cycle machinery. Bioessays. 2000;22:818–26. - PubMed
-
- Scholl FA, Dumesic PA, Khavari PA. Mek1 alters epidermal growth and differentiation. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6035–40. - PubMed
-
- Scholl FA, Dumesic PA, Khavari PA. Effects of active MEK1 expression in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2005;230:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Mansour SJ, Matten WT, Hermann AS, et al. Transformation of mammalian cells by constitutively active MAP kinase kinase. Science. 1994;265:966–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

