Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34
- PMID: 20570894
- PMCID: PMC2913706
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0655
Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34
Abstract
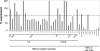
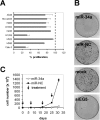
Tumor suppressor microRNAs (miRNA) provide a new opportunity to treat cancer. This approach, "miRNA replacement therapy," is based on the concept that the reintroduction of miRNAs depleted in cancer cells reactivates cellular pathways that drive a therapeutic response. Here, we describe the development of a therapeutic formulation using chemically synthesized miR-34a and a lipid-based delivery vehicle that blocks tumor growth in mouse models of non-small-cell lung cancer. This formulation is effective when administered locally or systemically. The antioncogenic effects are accompanied by an accumulation of miR-34a in the tumor tissue and downregulation of direct miR-34a targets. Intravenous delivery of formulated miR-34a does not induce an elevation of cytokines or liver and kidney enzymes in serum, suggesting that the formulation is well tolerated and does not induce an immune response. The data provide proof of concept for the systemic delivery of a synthetic tumor suppressor mimic, obviating obstacles associated with viral-based miRNA delivery and facilitating a rapid route for miRNA replacement therapy into the clinic.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures
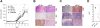

References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66. - PubMed
-
- Petrocca F, Lieberman J. Micromanipulating cancer: microRNA-based therapeutics? RNA Biol. 2009;6:335–40. - PubMed
-
- Tong AW, Nemunaitis J. Modulation of miRNA activity in human cancer: a new paradigm for cancer gene therapy? Cancer Gene Ther. 2008;15:341–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

