Altered dynamics of intestinal cell maturation in Apc1638N/+ mice
- PMID: 20570902
- PMCID: PMC2906237
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4593
Altered dynamics of intestinal cell maturation in Apc1638N/+ mice
Abstract
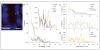
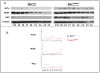
Novel imaging of active transcription sites in interphase nuclei of intestinal epithelial cells in situ showed that key genes associated with Wnt and Notch signaling were dynamically regulated as the cells underwent normal maturation during their migration along the mouse crypt-villus axis (CVA). However, oscillating patterns of activation of these genes were displaced along this axis in the histologically normal intestinal mucosa of Apc(1638N/+) mice before tumor development. Gene expression profiling then showed that the normal reprogramming of cells along the CVA was dampened in the Apc(1638N/+) mice, with an overrepresentation of c-myc target genes among those loci affected in the mutant mice. Moreover, in the Apc(1638N/+) mice, there was a perturbed pattern of expression of lineage-specific markers along the CVA consistent with transcription site repression of the Math1 gene, and genes encoding enzymes of every step of the tricarboxylic acid cycle were downregulated in the crypt of Apc(1638N/+) mice compared with WT, but not in the villus. These changes may alter energy metabolism and generate a pseudohypoxic state, suggested by elevated expression of Hif1alpha and its target genes. Thus, although intestinal tumors develop in Apc(1638N/+) mice on focal loss or inactivation of the WT allele, our results show that in the Apc(1638N/+) mouse, inheritance of only a single WT Apc allele perturbs the dynamic and complex reprogramming underlying normal cell maturation, which links epithelial function and homeostasis with architectural organization of the intestine.
Copyright 2010 AACR.
Figures



References
-
- Mariadason JM, Nicholas C, L’Italien KE, Zhuang M, Smartt HJ, Heerdt BG, et al. Gene expression profiling of intestinal epithelial cell maturation along the crypt-villus axis. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1081–8. - PubMed
-
- Smartt H, Guilmeau S, Nasser S, Nicholas C, Bancroft L, Simpson S, et al. p27kip1 regulates cdk2 activity in the proliferating zone of the mouse intestinal epithelium: potential role in neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2007;207:232–43. - PubMed
-
- Su L-K, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Preisinger AC, Moser AR, Luongo C, et al. Multiple intestinal neoplasia caused by a mutation in the murine homolog of the APC gene. Science. 1992;256:668–70. - PubMed
-
- Levy DB, Smith KJ, Beazer-Barclay Y, Hamilton SR, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Inactivation of Both APC alleles in human and mouse tumors. Cancer Res. 1994;54:5953–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 GM080247/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA114265/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB002060/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA083208/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R33CA-083208/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM80247/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA100926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P013330/PHS HHS/United States
- P30 CA013330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA114265/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA135561/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- EB2060/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA135561/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA100926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

