Human immune system development and rejection of human islet allografts in spontaneously diabetic NOD-Rag1null IL2rgammanull Ins2Akita mice
- PMID: 20570944
- PMCID: PMC2927949
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0323
Human immune system development and rejection of human islet allografts in spontaneously diabetic NOD-Rag1null IL2rgammanull Ins2Akita mice
Abstract
Objective: To create an immunodeficient mouse model that spontaneously develops hyperglycemia to serve as a diabetic host for human islets and stem cell-derived beta-cells in the absence or presence of a functional human immune system.
Research design and methods: We backcrossed the Ins2(Akita) mutation onto the NOD-Rag1(null) IL2rgamma(null) strain and determined 1) the spontaneous development of hyperglycemia, 2) the ability of human islets, mouse islets, and dissociated mouse islet cells to restore euglycemia, 3) the generation of a human immune system following engraftment of human hematopoietic stem cells, and 4) the ability of the humanized mice to reject human islet allografts.
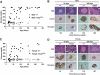
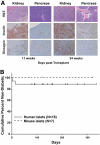
Results: We confirmed the defects in innate and adaptive immunity and the spontaneous development of hyperglycemia conferred by the IL2rgamma(null), Rag1(null), and Ins2(Akita) genes in NOD-Rag1(null) IL2rgamma(null) Ins2(Akita) (NRG-Akita) mice. Mouse and human islets restored NRG-Akita mice to normoglycemia. Insulin-positive cells in dissociated mouse islets, required to restore euglycemia in chemically diabetic NOD-scid IL2rgamma(null) and spontaneously diabetic NRG-Akita mice, were quantified following transplantation via the intrapancreatic and subrenal routes. Engraftment of human hematopoietic stem cells in newborn NRG-Akita and NRG mice resulted in equivalent human immune system development in a normoglycemic or chronically hyperglycemic environment, with >50% of engrafted NRG-Akita mice capable of rejecting human islet allografts.
Conclusions: NRG-Akita mice provide a model system for validation of the function of human islets and human adult stem cell, embryonic stem cell, or induced pluripotent stem cell-derived beta-cells in the absence or presence of an alloreactive human immune system.
Figures

References
-
- Gurdon JB, Melton DA. Nuclear reprogramming in cells. Science 2008;322:1811–1815 - PubMed
-
- Zhou Q, Melton DA. Pathways to new beta cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 2008;73:175–181 - PubMed
-
- Fellous TG, Guppy NJ, Brittan M, Alison MR. Cellular pathways to beta-cell replacement. Diabete Metab Res Rev 2007;23:87–99 - PubMed
-
- Sordi V, Bertuzzi F, Piemonti L. Diabetes mellitus: an opportunity for therapy with stem cells? Regen Med 2008;3:377–397 - PubMed
-
- Kroon E, Martinson LA, Kadoya K, Bang AG, Kelly OG, Eliazer S, Young H, Richardson M, Smart NG, Cunningham J, Agulnick AD, D'Amour KA, Carpenter MK, Baetge EE. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 2008;26:443–452 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI46629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK69603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK53006/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK032520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK072473/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK32520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK66636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK089572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA34196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI042845/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK068854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000666/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI046629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK72473/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK68854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK053006/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL077642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI042845/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

