Thrombin stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis in vascular smooth muscle is mediated by protease-activated receptor-1 transactivation of the transforming growth factor beta type I receptor
- PMID: 20571025
- PMCID: PMC2930678
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092767
Thrombin stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis in vascular smooth muscle is mediated by protease-activated receptor-1 transactivation of the transforming growth factor beta type I receptor
Abstract
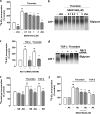
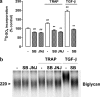
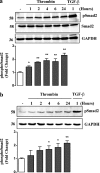
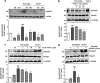
Growth factors modify the structure of the glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains on biglycan leading to enhanced LDL binding. G-protein receptor-coupled agonists such as thrombin, signal changes the structure of proteoglycans produced by vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). One component of classical G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling invokes transactivation of protein tyrosine kinase receptors such as the epidermal growth factor receptor. Serine/threonine receptor growth factors such as transforming growth factor-(TGF)-beta are potent activators of proteoglycan synthesis. We have used the model of proteoglycan synthesis to demonstrate that the signaling paradigm of GPCR signaling can be extended to include the transactivation of serine/threonine receptor, specifically the TGF-beta type I receptor (TbetaRI) also known as activin-like kinase (ALK) V. Thrombin stimulated elongation of GAG chains and increased proteoglycan core protein expression and these responses were blocked by the TbetaRI antagonist, SB431542 and TbetaRI siRNA knockdown, as well as several protease-activated receptor (PAR)-1 antagonists. The canonical downstream response to TGF-beta is increased C-terminal phosphorylation of the transcription factor Smad2 generating phospho-Smad2C (phosphorylation of Smad2 C-terminal region). Thrombin stimulated increased phospho-Smad2C levels, and the response was blocked by SB431542 and JNJ5177094. The proteolytically inactive thrombin mimetic thrombin-receptor activating peptide also stimulated an increase in cytosolic phospho-Smad2C. Signaling pathways for growth factor regulated proteoglycan synthesis represent therapeutic targets for the prevention of atherosclerosis, but the novel finding of a GPCR-mediated transactivation of a serine/threonine growth factor receptor almost certainly has implications well beyond the synthesis of proteoglycans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelin-1 stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis in vascular smooth muscle is mediated by endothelin receptor transactivation of the transforming growth factor-[beta] type I receptor.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;56(4):360-8. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181ee6811. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20625315
-
Thrombin-mediated proteoglycan synthesis utilizes both protein-tyrosine kinase and serine/threonine kinase receptor transactivation in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):7410-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400259. Epub 2013 Jan 18. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23335513 Free PMC article.
-
Smad and p38 MAP kinase-mediated signaling of proteoglycan synthesis in vascular smooth muscle.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 21;283(12):7844-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703125200. Epub 2008 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18223258
-
GPCR responses in vascular smooth muscle can occur predominantly through dual transactivation of kinase receptors and not classical Gαq protein signalling pathways.Life Sci. 2013 May 30;92(20-21):951-6. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.03.017. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23583575 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-β regulation of proteoglycan synthesis in vascular smooth muscle: contribution to lipid binding and accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetes.J Diabetes. 2010 Dec;2(4):233-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2010.00089.x. J Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20923499 Review.
Cited by
-
TGFβ receptor I transactivation mediates stretch-induced Pak1 activation and CTGF upregulation in mesangial cells.J Cell Sci. 2013 Aug 15;126(Pt 16):3697-712. doi: 10.1242/jcs.126714. Epub 2013 Jun 18. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23781022 Free PMC article.
-
Protease-activated receptor-1 deficiency protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in mice.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 13;6:33030. doi: 10.1038/srep33030. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27618774 Free PMC article.
-
Protease-activated receptors in health and disease.Physiol Rev. 2023 Jan 1;103(1):717-785. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00044.2021. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 35901239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteinase-activated receptors (PARs) - focus on receptor-receptor-interactions and their physiological and pathophysiological impact.Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Nov 11;11:86. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-86. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 24215724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expansion of GPCR transactivation-dependent signalling to include serine/threonine kinase receptors represents a new cell signalling frontier.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Feb;72(4):799-808. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1775-0. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25384733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hozawa A., Folsom A. R., Sharrett A. R., Chambless L. E. (2007) Arch. Intern Med. 167, 573–579 - PubMed
-
- Nakashima Y., Fujii H., Sumiyoshi S., Wight T. N., Sueishi K. (2007) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27, 1159–1165 - PubMed
-
- Little P. J., Osman N., O'Brien K. D. (2008) Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 19, 448–454 - PubMed
-
- Ross R. (1999) N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 115–126 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

