A Pseudomonas syringae ADP-ribosyltransferase inhibits Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases
- PMID: 20571112
- PMCID: PMC2910962
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.110.075697
A Pseudomonas syringae ADP-ribosyltransferase inhibits Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases
Abstract
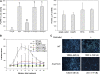
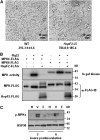
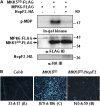
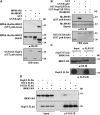
The successful recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) as a danger signal is crucial for plants to fend off numerous potential pathogenic microbes. The signal is relayed through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MPK) cascades to activate defenses. Here, we show that the Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopF2 can interact with Arabidopsis thaliana MAP KINASE KINASE5 (MKK5) and likely other MKKs to inhibit MPKs and PAMP-triggered immunity. Inhibition of PAMP-induced MPK phosphorylation was observed when HopF2 was delivered naturally by the bacterial type III secretion system. In addition, HopF2 Arg-71 and Asp-175 residues that are required for the interaction with MKK5 are also necessary for blocking MAP kinase activation, PAMP-triggered defenses, and virulence function in plants. HopF2 can inactivate MKK5 and ADP-ribosylate the C terminus of MKK5 in vitro. Arg-313 of MKK5 is required for ADP-ribosylation by HopF2 and MKK5 function in the plant cell. Together, these results indicate that MKKs are important targets of HopF2.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopF2 suppresses Arabidopsis stomatal immunity.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 11;9(12):e114921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114921. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25503437 Free PMC article.
-
The Pseudomonas syringae effector HopF2 suppresses Arabidopsis immunity by targeting BAK1.Plant J. 2014 Jan;77(2):235-45. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12381. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24237140 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial effector HopF2 suppresses arabidopsis innate immunity at the plasma membrane.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011 May;24(5):585-93. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-07-10-0150. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011. PMID: 21198360 Free PMC article.
-
The type III effector HopF2Pto targets Arabidopsis RIN4 protein to promote Pseudomonas syringae virulence.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 2;107(5):2349-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904739107. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133879 Free PMC article.
-
The multilevel and dynamic interplay between plant and pathogen.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Apr;4(4):283-93. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.4.8155. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. Retraction in: Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Jun;4(6):568. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.6.8867. PMID: 19794843 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
AvrRpm1 missense mutations weakly activate RPS2-mediated immune response in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042633. Epub 2012 Aug 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22880057 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of long non-coding RNAs in plant immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2023 May 11;19(5):e1011340. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011340. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37167200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Biosurveillance of the Kiwifruit Pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae Biovar 3 Reveals Adaptation to Selective Pressures in New Zealand Orchards.Mol Plant Pathol. 2025 Feb;26(2):e70056. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70056. Mol Plant Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39915983 Free PMC article.
-
Salicylic acid: an old hormone up to new tricks.Mol Plant Pathol. 2013 Aug;14(6):623-34. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12035. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Mol Plant Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23621321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of NOI-domain containing proteins in plant immune signaling.BMC Genomics. 2013 May 14;14:327. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-327. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23672422 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asai T., Tena G., Plotnikova J., Willmann M.R., Chiu W.-L., Gomez-Gomez L., Boller T., Ausubel F.M., Sheen J. (2002). MAP kinase signaling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415: 977–983 - PubMed
-
- Bergmann D.C., Lukowitz W., Somerville C.R. (2004). Stomatal development and pattern controlled by a MAPKK kinase. Science 304: 1494–1497 - PubMed
-
- Boller T., Felix G. (2009). A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 60: 379–406 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

