Effects of cholesterol and its 24S-OH and 25-OH oxysterols on choline acetyltransferase-positive neurons in brain slices
- PMID: 20571288
- PMCID: PMC4311142
- DOI: 10.1159/000314333
Effects of cholesterol and its 24S-OH and 25-OH oxysterols on choline acetyltransferase-positive neurons in brain slices
Abstract
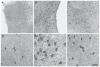
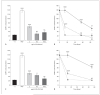
In Alzheimer's disease (AD) neurons expressing the enzyme choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) degenerate and a loss of cholinergic activity directly correlates with cognitive decline. Recent studies have suggested that cholesterol plays a role in AD. The aim of the present study was to explore if cholesterol and its oxysterols, 24S-hydroxycholesterol (24S-OH Chol) and 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-OH Chol), affect ChAT-positive neurons in organotypic brain slices of the basal nucleus of Meynert (nBM). We showed that slices expressed approximately 140 ChAT-positive neurons/slice after 2 weeks when incubated with nerve growth factor (NGF). This number markedly decreased when incubated without NGF to approximately 20 neurons/slice. Cholesterol and 24S-OH Chol delayed this decrease in ChAT-positive neurons. In contrast, 25-OH Chol induced a decline in ChAT-positive neurons in 2-week-old slices within 4 days. The effects of cholesterol and its oxysterols were exhibited in a dose- and time-dependent way. Our results show that cholesterol and 24S-OH Chol delays the decrease in ChAT-positive neurons, while 25-OH Chol rapidly decreases ChAT expression, suggesting differential mechanisms on ChAT expression in cholinergic nBM neurons.
Copyright 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethanol transiently suppresses choline-acetyltransferase in basal nucleus of Meynert slices.Brain Res. 2012 Jun 12;1459(3):35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.04.020. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22560095 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons associated with aging and long-term loss of ovarian function.Exp Neurol. 1998 Jun;151(2):289-302. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1998.6789. Exp Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9628764
-
Nerve growth factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor restore the cholinergic neuronal phenotype in organotypic brain slices of the basal nucleus of Meynert.Neuroscience. 2001;102(1):129-38. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00452-8. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11226676
-
Melatonin Supports the Survival of Cholinergic Neurons in Organotypic Brain Slices of the Basal Nucleus of Meynert.Pharmacology. 2023;108(2):204-212. doi: 10.1159/000527887. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Pharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36724742
-
Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterases in Alzheimer's disease.Fed Proc. 1986 Dec;45(13):2982-8. Fed Proc. 1986. PMID: 2430839 Review.
Cited by
-
Mini-ruby is rapidly taken up by neurons and astrocytes in organotypic brain slices.Neurochem Res. 2011 Oct;36(10):1817-23. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0499-x. Epub 2011 May 22. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21604155 Free PMC article.
-
The Controversial Role of 24-S-Hydroxycholesterol in Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 7;10(5):740. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050740. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homocysteine has anti-inflammatory properties in a hypercholesterolemic rat model in vivo.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2012 Apr;49(4):456-63. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22425561 Free PMC article.
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol as a Signaling Molecule of the Nervous System.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022 Jun;87(6):524-537. doi: 10.1134/S0006297922060049. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022. PMID: 35790411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant sterols and cholesterol metabolism are associated with five-year cognitive decline in the elderly population.iScience. 2023 Apr 24;26(6):106740. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106740. eCollection 2023 Jun 16. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37250771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Winkler J, Thal LJ, Gage FH, Fisher LJ. Cholinergic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Med. 1998;76:555–567. - PubMed
-
- Schliebs R, Arendt T. The significance of the cholinergic system in the brain during aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm. 2006;113:1625–1644. - PubMed
-
- Sassin I, Schultz C, Thal DR, Rüb U, Arai K, Braak E, Braak H. Evolution of Alzheimer’s disease-related cytoskeletal changes in the basal nucleus of Meynert. Acta Neuropathol. 2000;100:259–269. - PubMed
-
- Simons M, Keller P, Dichgans J, Schulz JB. Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 2001;57:1089–1093. - PubMed
-
- Puglielli L, Tanzi RE, Kovacs DM. Alzheimer’s disease: the cholesterol connection. Nature Neurosci. 2003;6:345–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

