Affective cognition and its disruption in mood disorders
- PMID: 20571485
- PMCID: PMC3055516
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2010.77
Affective cognition and its disruption in mood disorders
Abstract
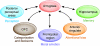
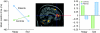
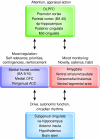
In this review, we consider affective cognition, responses to emotional stimuli occurring in the context of cognitive evaluation. In particular, we discuss emotion categorization, biasing of memory and attention, as well as social/moral emotion. We discuss limited neuropsychological evidence suggesting that affective cognition depends critically on the amygdala, ventromedial frontal cortex, and the connections between them. We then consider neuroimaging studies of affective cognition in healthy volunteers, which have led to the development of more sophisticated neural models of these processes. Disturbances of affective cognition are a core and specific feature of mood disorders, and we discuss the evidence supporting this claim, both from behavioral and neuroimaging perspectives. Serotonin is considered to be a key neurotransmitter involved in depression, and there is a considerable body of research exploring whether serotonin may mediate disturbances of affective cognition. The final section presents an overview of this literature and considers implications for understanding the pathophysiology of mood disorder as well as developing and evaluating new treatment strategies.
Figures

References
-
- Abramson LY, Seligman ME, Teasdale JD.1978Learned helplessness in humans: critique and reformulation J Abnorm Psychol 8749–74.This seminal paper emphasizes global, stable and internal attributions for negative outcomes as key to understanding vulnerability to depression. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Baron-Cohen S, Tranel D. Impaired recognition of social emotions following amygdala damage. J Cogn Neurosci. 2002;14:1264–1274. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Cahill L, Schul R, Babinsky R. Impaired declarative memory for emotional material following bilateral amygdala damage in humans. Learn Mem. 1997;4:291–300. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Tranel D. Impaired judgments of sadness but not happiness following bilateral amygdala damage. J Cogn Neurosci. 2004;16:453–462. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Tranel D, Damasio AR. The human amygdala in social judgment. Nature. 1998;393:470–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

