Overlapping functions of Hdac1 and Hdac2 in cell cycle regulation and haematopoiesis
- PMID: 20571512
- PMCID: PMC2928690
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.136
Overlapping functions of Hdac1 and Hdac2 in cell cycle regulation and haematopoiesis
Abstract
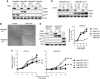
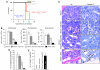
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) counterbalance acetylation of lysine residues, a protein modification involved in numerous biological processes. Here, Hdac1 and Hdac2 conditional knock-out alleles were used to study the function of class I Hdac1 and Hdac2 in cell cycle progression and haematopoietic differentiation. Combined deletion of Hdac1 and Hdac2, or inactivation of their deacetylase activity in primary or oncogenic-transformed fibroblasts, results in a senescence-like G(1) cell cycle arrest, accompanied by up-regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(Cip). Notably, concomitant genetic inactivation of p53 or p21(Cip) indicates that Hdac1 and Hdac2 regulate p53-p21(Cip)-independent pathways critical for maintaining cell cycle progression. In vivo, we show that Hdac1 and Hdac2 are not essential for liver homeostasis. In contrast, total levels of Hdac1 and Hdac2 in the haematopoietic system are critical for erythrocyte-megakaryocyte differentiation. Dual inactivation of Hdac1 and Hdac2 results in apoptosis of megakaryocytes and thrombocytopenia. Together, these data indicate that Hdac1 and Hdac2 have overlapping functions in cell cycle regulation and haematopoiesis. In addition, this work provides insights into mechanism-based toxicities observed in patients treated with HDAC inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Brand M, Ranish JA, Kummer NT, Hamilton J, Igarashi K, Francastel C, Chi TH, Crabtree GR, Aebersold R, Groudine M (2004) Dynamic changes in transcription factor complexes during erythroid differentiation revealed by quantitative proteomics. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 73–80 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R (2002) Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell 2: 243–247 - PubMed
-
- Campisi J (2005) Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell 120: 513–522 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

