Focal adhesion kinase is essential for cardiac looping and multichamber heart formation
- PMID: 20572259
- PMCID: PMC3618911
- DOI: 10.1002/dvg.20650
Focal adhesion kinase is essential for cardiac looping and multichamber heart formation
Abstract
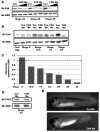
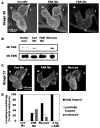
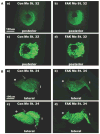
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a critical mediator of matrix- and growth factor-induced signaling during development. Myocyte-restricted FAK deletion in mid-gestation mice results in impaired ventricular septation and cardiac compaction. However, whether FAK regulates early cardiogenic steps remains unknown. To explore a role for FAK in multi-chambered heart formation, we utilized anti-sense morpholinos to deplete FAK in Xenopus laevis. Xenopus FAK morphants exhibited impaired cardiogenesis, pronounced pericardial edema, and lethality by tadpole stages. Spatial-temporal assessment of cardiac marker gene expression revealed that FAK was not necessary for midline migration, differentiation, fusion of cardiac precursors, or linear heart tube formation. However, myocyte proliferation was significantly reduced in FAK morphant heart tubes and these tubes failed to undergo proper looping morphogenesis. Collectively our data imply that FAK plays an essential role in chamber outgrowth and looping morphogenesis likely stimulated by fibroblast growth factors (and possibly other) cardiotrophic factors.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




Comment in
-
Highlighted article: "Focal adhesion kinase is essential for cardiac looping and multi-chamber heart formation" by Doherty, Conlon, Mack, and Taylor.Genesis. 2010 Aug;48(8):465. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20660. Genesis. 2010. PMID: 20730917 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Highlighted article: "Focal adhesion kinase is essential for cardiac looping and multi-chamber heart formation" by Doherty, Conlon, Mack, and Taylor.Genesis. 2010 Aug;48(8):465. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20660. Genesis. 2010. PMID: 20730917 No abstract available.
-
Focal adhesion kinase promotes integrin adhesion dynamics necessary for chemotropic turning of nerve growth cones.J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 21;31(38):13585-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2381-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21940449 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase mediates MEF2 and c-Jun activation by stretch: role in the activation of the cardiac hypertrophic genetic program.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Oct 1;68(1):87-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.05.011. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15961069
-
Focal adhesion kinase -- the basis of local hypertrophic signaling domains.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Feb;52(2):485-92. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.06.021. Epub 2011 Jul 2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 21749874 Review.
-
ErbB/integrin signaling interactions in regulation of myocardial cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Apr;1833(4):909-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.12.007. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23261977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Of form and function: Early cardiac morphogenesis across classical and emerging model systems.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct;118:107-118. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.04.025. Epub 2021 May 14. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33994301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of collagen type IV regulation by focal adhesion kinase during retained fetal membranes in dairy cows.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 6;14(1):23250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74947-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39370419 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac looping may be driven by compressive loads resulting from unequal growth of the heart and pericardial cavity. Observations on a physical simulation model.Front Physiol. 2014 Apr 4;5:112. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00112. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24772086 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Adhesion's Role in Cardiomyocytes Function: From Cardiomyogenesis to Mechanotransduction.Cells. 2024 Apr 10;13(8):664. doi: 10.3390/cells13080664. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-culture with neonatal cardiomyocytes enhances the proliferation of iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes via FAK/JNK signaling.BMC Dev Biol. 2016 May 4;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s12861-016-0112-2. BMC Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27141946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brade T, Gessert S, Kuhl M, Pandur P. The amphibian second heart field: Xenopus islet-1 is required for cardiovascular development. Dev Biol. 2007;311:297–310. - PubMed
-
- Choi M, Stottmann RW, Yang YP, Meyers EN, Klingensmith J. The bone morphogenetic protein antagonist noggin regulates mammalian cardiac morphogenesis. Circ Res. 2007;100:220–228. - PubMed
-
- David JP, Victoria LTB, Takashi M. Epicardium is required for the full rate of myocyte proliferation and levels of expression of myocyte mitogenic factors FGF2 and its receptor. FGFR-1, but not for transmural myocardial patterning in the embryonic chick heart. Dev Dynamics. 2003;228:161–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL-071054/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102446/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081844/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DE-018825/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- HL-081844/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 089641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL070953/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018825/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070953/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL69768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071054/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

