Distribution of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor receptor alpha-1 in the brain of adult zebrafish
- PMID: 20572899
- PMCID: PMC2913026
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01254.x
Distribution of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor receptor alpha-1 in the brain of adult zebrafish
Erratum in
- J Anat. 2011 Mar;218(3):362. Carla, Lucini [corrected to Lucini, Carla]; Bruna, Facello [corrected to Facello, Bruna]; Lucianna, Maruccio [corrected to Maruccio, Lucianna]; Fernanda, Langellotto [corrected to Langellotto, Fernanda]; Paolo, Sordino [corrected to Sordino, Paolo]; Lucian
Abstract
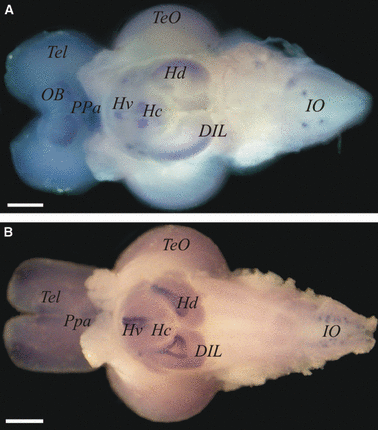
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a potent trophic factor for several types of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The biological activity of GDNF is mediated by a multicomponent receptor complex that includes a common transmembrane signaling component (the rearranged during transfection (RET) proto-oncogene product, a tyrosine kinase receptor) as well as a GDNF family receptor alpha (GFRalpha) subunit, a high-affinity glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked binding element. Among the four known GFRalpha subunits, GFRalpha1 preferentially binds to GDNF. In zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos, the expression of the GFRalpha1a and GFRalpha1b genes has been shown in primary motor neurons, the kidney, and the enteric nervous system. To examine the activity of GFRalpha in the adult brain of a lower vertebrate, we have investigated the localization of GFRalpha1a and GFRalpha1b mRNA and the GFRalpha1 protein in zebrafish. GFRalpha1a and GFRalpha1b transcripts were observed in brain extracts by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Whole-mount in-situ hybridization experiments revealed a wide distribution of GFRalpha1a and GFRalpha1b mRNAs in various regions of the adult zebrafish brain. These included the olfactory bulbs, dorsal and ventral telencephalic area (telencephalon), preoptic area, dorsal and ventral thalamus, posterior tuberculum and hypothalamus (diencephalon), optic tectum (mesencephalon), cerebellum, and medulla oblongata (rhombencephalon). Finally, expression patterns of the GFRalpha1 protein, detected immunohistochemically, correlated well with the mRNA expression and provided further insights into translational activity at the neuroanatomical level. In conclusion, the current study demonstrated that the presence of GFRalpha1 persists beyond the embryonic development of the zebrafish brain and, together with the GDNF ligand, is probably implicated in the brain physiology of an adult teleost fish.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MicroRNA regulation of central glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) signalling in depression.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Feb 17;5(2):e511. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.11. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25689572 Free PMC article.
-
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the brain of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio).Histol Histopathol. 2008 Mar;23(3):251-61. doi: 10.14670/HH-23.251. Histol Histopathol. 2008. PMID: 18072082
-
Expression of GFRalpha1 receptor splicing variants with different biochemical properties is modulated during kidney development.Cell Signal. 2004 Dec;16(12):1425-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.05.006. Cell Signal. 2004. PMID: 15381258
-
Novel functions and signalling pathways for GDNF.J Cell Sci. 2003 Oct 1;116(Pt 19):3855-62. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00786. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12953054 Review.
-
Evolution of the GDNF family ligands and receptors.Brain Behav Evol. 2006;68(3):181-90. doi: 10.1159/000094087. Brain Behav Evol. 2006. PMID: 16912471 Review.
References
-
- Arvidsson A, Kokaia Z, Airaksinen MS, et al. Stroke induced widespread changes of gene expression for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family receptors in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience. 2001;106:27–41. - PubMed
-
- Becker CG, Becker T. Adult zebrafish as a model for successful central nervous system regeneration. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2008;26:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Burazin TC, Gundlach AL. Localization of GDNF/neurturin receptor (c-ret, GFRalpha-1 and GFRalpha-2) mRNAs in postnatal rat brain: differential regional and temporal expression in hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999;73:151–171. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZY, Chai YF, Cao L, et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor enhances axonal regeneration following sciatic nerve transection in adult rats. Brain Res. 2001;902:272–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

