Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions of echinacea and policosanol with warfarin in healthy subjects
- PMID: 20573086
- PMCID: PMC2856051
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03620.x
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions of echinacea and policosanol with warfarin in healthy subjects
Abstract
Aims: This study investigated the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions of echinacea and policosanol with warfarin in healthy subjects.
Methods: This was an open-label, randomized, three-treatment, cross-over, clinical trial in healthy male subjects (n= 12) of known CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype who received a single oral dose of warfarin alone or after 2 weeks of pre-treatment with each herbal medicine at recommended doses. Pharmacodynamic (INR, platelet activity) and pharmacokinetic (warfarin enantiomer concentrations) end points were evaluated.
Results: The apparent clearance of (S)-warfarin (90% CI of ratio; 1.01, 1.18) was significantly higher during concomitant treatment with echinacea but this did not lead to a clinically significant change in INR (90% CI of AUC of INR; 0.91, 1.31). Policosanol did not significantly affect warfarin enantiomer pharmacokinetics or warfarin response. Neither echinacea nor policosanol had a significant effect on platelet aggregation after 2 weeks of pre-treatment with the respective herbal medicines.
Conclusion: Echinacea significantly reduced plasma concentrations of S-warfarin. However, neither echinacea nor policosanol significantly affected warfarin pharmacodynamics, platelet aggregation or baseline clotting status in healthy subjects.
Figures
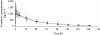
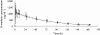
Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamic interaction of warfarin with cranberry but not with garlic in healthy subjects.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;154(8):1691-700. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.210. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18516070 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of ginkgo and ginger on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of warfarin in healthy subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Apr;59(4):425-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02322.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15801937 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of nilotinib on single-dose warfarin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: a randomized, single-blind, two-period crossover study in healthy subjects.Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31(3):169-79. doi: 10.2165/11538700-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2011. PMID: 21184622 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacogenetic differences between warfarin, acenocoumarol and phenprocoumon.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Dec;100(6):1052-7. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 19132230 Review.
-
Pharmacogenetics of oral anticoagulants: a basis for dose individualization.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47(9):565-94. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200847090-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008. PMID: 18698879 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of potential harmful interactions between anticoagulant/antiplatelet agents and Chinese herbal medicines.PLoS One. 2013 May 9;8(5):e64255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064255. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23671711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary supplements and bleeding.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2022 Sep 15;35(6):802-807. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2022.2121575. eCollection 2022. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2022. PMID: 36304597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic Interactions between Herbal Medicines and Drugs: Their Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance.Life (Basel). 2020 Jul 4;10(7):106. doi: 10.3390/life10070106. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32635538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Risk and Benefits of Concomitantly Using Herbal Medicines and Conventional Medicines: From the Perspectives of Evidence Based on Randomized Controlled Trials and Clinical Risk Management.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:9296404. doi: 10.1155/2017/9296404. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28491115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of commonly used dietary supplements with cardiovascular drugs: a systematic review.Syst Rev. 2012 May 31;1:26. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-1-26. Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22651380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aquilante CL, Langaee TY, Lopez LM, Yarandi HN, Tromberg JS, Mohuczy D, Gaston KL, Waddell CD, Chirico MJ, Johnson JA. Influence of coagulation factor, vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1, and cytochrome P450 2C9 gene polymorphisms on warfarin dose requirements. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;79:291–302. - PubMed
-
- Muszkat M, Blotnik S, Elami A, Krasilnikov I, Caraco Y. Warfarin metabolism and anticoagulant effect: a prospective, observational study of the impact of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism in the presence of drug-disease and drug-drug interactions. Clin Ther. 2007;29:427–37. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J, Anderson LA, Gibbons S, Phillipson JD. Echinacea species (Echinacea angustifolia (DC.) Hell., Echinacea pallida (Nutt.) Nutt., Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench): a review of their chemistry, pharmacology and clinical properties. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005;57:929–54. - PubMed
-
- Matthias A, Addison RS, Agnew LL, Bone KM, Watson K, Lehmann RP. Comparison of echinacea alkylamide pharmacokinetics between liquid and tablet preparations. Phytomedicine. 2007;14:587–90. - PubMed
-
- Matthias A, Addison RS, Penman KG, Dickinson RG, Bone KM, Lehmann RP. Echinacea alkamide disposition and pharmacokinetics in humans after tablet ingestion. Life Sci. 2005;77:2018–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

