Interpersonal circumplex descriptions of psychosocial risk factors for physical illness: application to hostility, neuroticism, and marital adjustment
- PMID: 20573134
- PMCID: PMC5045262
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2010.00641.x
Interpersonal circumplex descriptions of psychosocial risk factors for physical illness: application to hostility, neuroticism, and marital adjustment
Abstract
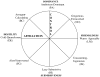
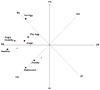
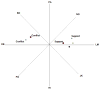
Personality risk factors for physical illness are typically studied individually and apart from risk factors reflecting the social environment, potentially fostering a piecemeal understanding of psychosocial influences on health. Because it can be used to describe both personality and social relationship processes, the interpersonal circumplex (IPC) provides an integrative approach to psychosocial risk. In 301 married couples we examined IPC correlates of 3 risk factor domains: anger, hostility, and aggressiveness; neuroticism; and marital adjustment. Risk factors displayed IPC locations ranging from hostile dominance (e.g., verbal aggressiveness, marital conflict) to hostility (e.g., anger) to hostile submissiveness (e.g., anxiety, depression); protective factors (marital satisfaction and support) reflected warmth or friendliness in the IPC. Similar descriptions were found using self-reports and spouse ratings of IPC dimensions, indicating that interpersonal styles associated with risk factors do not simply reflect common method variance. Findings identify interpersonal processes reflecting low affiliation or high hostility as a common component of risk and indicate distinctions among risk factors along the dominance dimension.
Figures






References
-
- Alden LE, Wiggins JS, Pincus AL. Construction of circumplex scales for the Inventory of Interpersonal Problems. Journal of Personality Assessment. 1990;55:521–536. - PubMed
-
- Barefoot JC, Dodge KA, Peterson BL, Dahlstrom WG, Williams RB., Jr The Cook–Medley Hostility Scale: Item content and ability to predict survival. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1989;51:46–57. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin LS, Rothweiler JC, Critchfield KL. The use of Structural Analysis of Social Behavior (SASB) as an assessment tool. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 2006;2:83–109. - PubMed
-
- Blascovich J, Tomaka J. The biopsychosocial model of arousal regulation. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology. 1996;28:1–51.
-
- Bolger N, Schilling EA. Personality and the problems of everyday life: The role of neuroticism in exposure and reactivity to daily stressors. Journal of Personality. 1991;59:355–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

