Anti-Asthma Simplified Herbal Medicine Intervention-induced long-lasting tolerance to allergen exposure in an asthma model is interferon-γ, but not transforming growth factor-β dependent
- PMID: 20573156
- PMCID: PMC2946973
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03545.x
Anti-Asthma Simplified Herbal Medicine Intervention-induced long-lasting tolerance to allergen exposure in an asthma model is interferon-γ, but not transforming growth factor-β dependent
Abstract
Background: Chronic allergic asthma is the result of a T-helper type 2 (Th2)-biased immune status. Current asthma therapies control symptoms in some patients, but a long-lasting therapy has not been established. Anti-Asthma Simplified Herbal Medicine Intervention (ASHMI™), a Chinese herbal formula, improved symptoms and lung function, and reduced Th2 responses in a controlled trial of patients with persistent moderate to severe asthma.
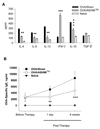
Objective: We evaluated the persistence of ASHMI™ beneficial effects following therapy in a murine model of chronic asthma and the immunological mechanisms underlying such effects. Methods BALB/c mice sensitized intraperitoneally with ovalbumin (OVA) received 3 weekly intratracheal OVA challenges to induce airway hyper-reactivity (AHR) and inflammation (OVA mice). Additionally, OVA mice were treated with ASHMI™ (OVA/ASHMI™) or water (OVA/sham) for 4 weeks, and then challenged immediately and 8 weeks post-therapy. In other experiments, OVA mice received ASHMI™ treatment with concomitant neutralization of IFN-γ or TGF-β. Effects on airway responses, cytokine- and OVA-specific IgE levels were determined 8 weeks post-therapy.
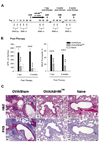
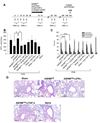
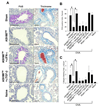
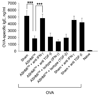
Results: Before treatment, OVA mice exhibited AHR and pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation following OVA challenge, which was almost completely resolved immediately after completing treatment with ASHMI™ and did not re-occur following OVA re-challenge up to 8 weeks post-therapy. Decreased allergen-specific IgE and Th2 cytokine levels, and increased IFN-γ levels also persisted at least 8 weeks post-therapy. ASHMI™ effects were eliminated by the neutralization of IFN-γ, but not TGF-β, during therapy.
Conclusion: ASHMI™ induced long-lasting post-therapy tolerance to antigen-induced inflammation and AHR. IFN-γ is a critical factor in ASHMI™ effects.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
Comment in
-
Chinese herbal anti-asthma tea to go!Clin Exp Allergy. 2010 Nov;40(11):1590-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03621.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010. PMID: 21039969 No abstract available.
References
-
- Braman SS. The global burden of asthma. Chest. 2006;130 4S–12S. - PubMed
-
- Lemanske RFJ. A review of the current guidelines for allergic rhinitis and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;101:S392–S396. - PubMed
-
- Hall IP. The beta-agonist controversy revisited. Lancet. 2004;363:183–184. - PubMed
-
- Guilbert TW, Morgan WJ, Zeiger RS, Mauger DT, Boehmer SJ, Szefler SJ, Bacharier LB, Lemanske RF, Jr, Strunk RC, Allen DB, Bloomberg GR, Heldt G, Krawiec M, Larsen G, Liu AH, Chinchilli VM, Sorkness CA, Taussig LM, Martinez FD. Long-term inhaled corticosteroids in preschool children at high risk for asthma. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1985–1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

